(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
Date of commencement of electronic provision measures: May 27, 2024
The 158th Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders
Other matters subject to the electronic provision measures
(Matters for which document delivery is omitted)
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Non-Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets
Notes to Non-Consolidated Financial Statements
(April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024)
Suzuki Motor Corporation

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
1
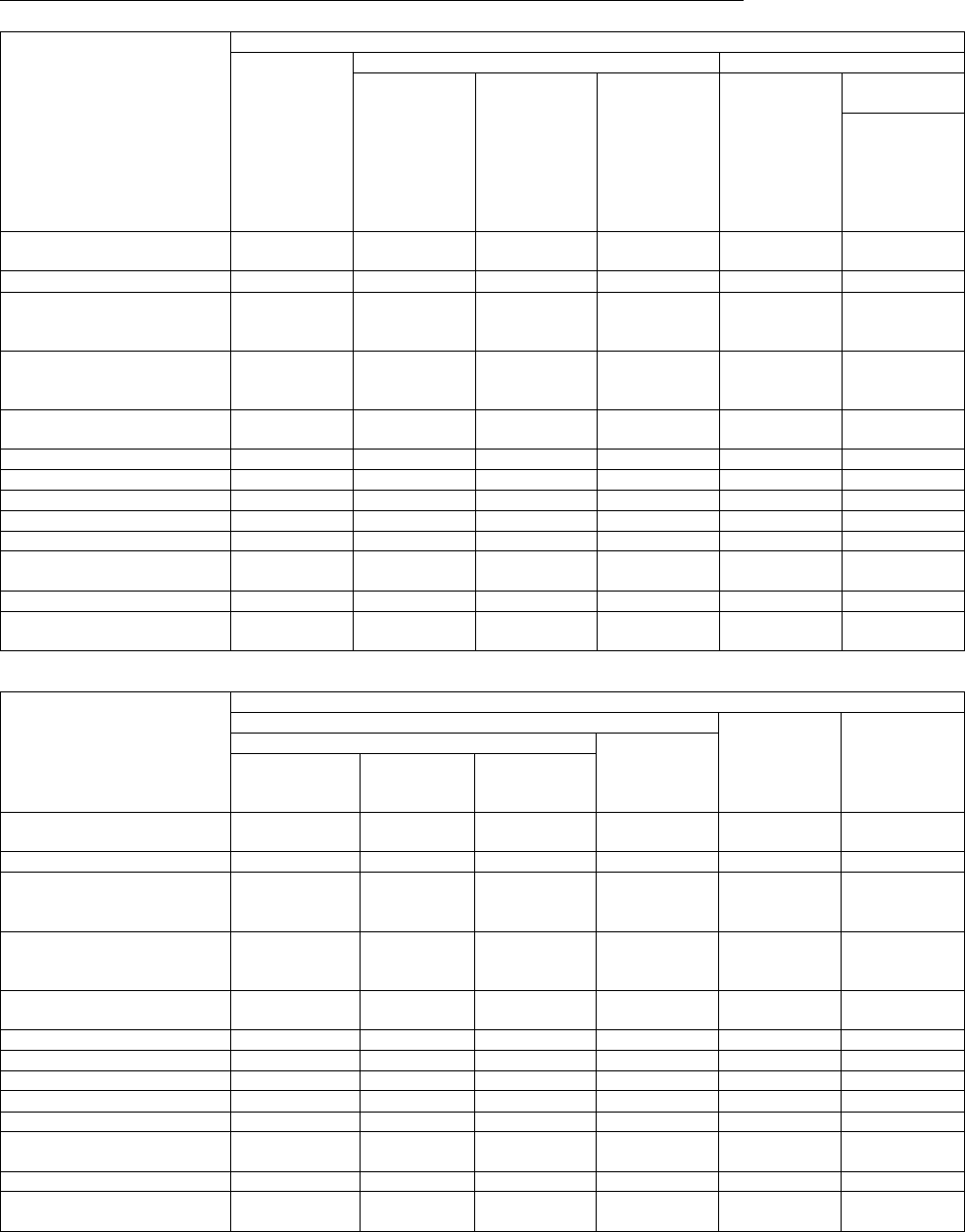
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets (April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024)
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Shareholders’ equity
Share capital
Capital surplus
Retained earnings
Treasury shares
Total shareholders’
equity
Balance at the beginning
of current fiscal year
138,370
138,180
1,813,209
(19,396)
2,070,363
Changes during period
Dividends of surplus
(50,836)
(50,836)
Profit attributable to
owners of parent
267,717
267,717
Purchase of shares of
consolidated
subsidiaries
(69,137)
(69,137)
Purchase of treasury
shares
(20,029)
(20,029)
Disposal of treasury
shares
42
125
168
Net changes in items
other than
shareholders’ equity
Total changes during
period
–
(69,095)
216,881
(19,903)
127,881
Balance at the end of
current fiscal year
138,370
69,084
2,030,090
(39,300)
2,198,245
Accumulated other comprehensive income
Share
acquisition
rights
Non-
controlling
interests
Total net
assets
Valuation
difference
on
Available-
for-sale
securities
Deferred
gains or
losses on
hedges
Foreign
currency
translation
adjustment
Remeasure-
ments of
defined
benefit plans
Total
accumulate
d other
comprehens
ive income
Balance at the beginning
of current fiscal year
117,885
(167)
(86,742)
(23,321)
7,653
41
430,561
2,508,620
Changes during period
Dividends of surplus
(50,836)
Profit attributable to
owners of parent
267,717
Purchase of shares of
consolidated
subsidiaries
(69,137)
Purchase of treasury
shares
(20,029)
Disposal of treasury
shares
168
Net changes in items
other than
shareholders’ equity
118,835
(16)
150,695
15,599
285,114
–
216,781
501,895
Total changes during
period
118,835
(16)
150,695
15,599
285,114
–
216,781
629,777
Balance at the end of
current fiscal year
236,720
(183)
63,953
(7,722)
292,768
41
647,342
3,138,397
[Note] Amounts less than one million yen are rounded down.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
2
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1.
Notes to Basic Significant Matters for Preparing Consolidated Financial Statements
(1)
Scope of consolidation
1)
Number of consolidated subsidiaries and name of main consolidated subsidiaries
Number of consolidated subsidiaries 119 companies
Name of main consolidated subsidiaries
Domestic ……… Suzuki Auto Parts Mfg. Co., Ltd.
Suzuki Motor Sales Kinki Inc.
Overseas ……… Magyar Suzuki Corporation Ltd.
SUZUKI ITALIA S.p.A.
Maruti Suzuki India Ltd.
Suzuki Motor Gujarat Private Ltd.
Suzuki Motorcycle India Private Ltd.
Pak Suzuki Motor Co., Ltd.
PT. Suzuki Indomobil Motor
TDS Lithium–Ion Battery Gujarat Private Ltd.
2)
Change in the scope of consolidation
Increase: 1 company Decrease: 2 companies
3)
Name of unconsolidated subsidiaries
Name of main unconsolidated subsidiaries ……… Suzuki Motor Co., Ltd.
Reason for exclusion:
Because these unconsolidated subsidiaries are small, and total influence by their total
assets, net sales, net income or loss (the amounts equivalent to the Company’s interest in
the companies) and retained earnings (the amounts equivalent to the Company’s interest
in the companies) on the consolidated financial statements are insignificant.
(2)
Application of the equity methods
1)
Number of companies accounted for using equity method and name of main companies
accounted for using equity method
Number of companies accounted for using equity method: 31 companies
Name of main companies accounted for using equity method ……… Krishna Maruti Ltd.
2)
Change in the scope of application of the equity method
Increase: 1 company Decrease: 2 companies
3)
Name of unconsolidated subsidiaries and entities that are not accounted for using equity method
Name of main unconsolidated subsidiaries and associates that are not accounted for
using equity method ............. Suzuki Motor Co., Ltd.
Reason for non–application:
In terms of net income or loss and retained earnings (the amounts equivalent to the
Company’s interest in the companies), influence of these companies on consolidated
financial statements is insignificant even if equity method is not applied to the companies,
and it is not important as a whole.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
3
(3)
Fiscal year and others of consolidated subsidiaries
1)
The number of consolidated subsidiaries for which the account settlement date is different
from the consolidated account settlement date (March 31) is as follows.
December 31……… 14, including Magyar Suzuki Corporation Ltd.
2)
The above consolidated subsidiaries are consolidated based on the financial statements on the
provisional settlement of accounts on the consolidated account settlement date.
(4)
Accounting policy
1)
Evaluation standards and evaluation methods of significant assets
(a) Securities
Available-for-sale securities…… Items other than equity securities for which market values
are unavailable:
Fair value method (The evaluation differences shall be
reported as a component of net assets, and sales costs shall
be calculated mainly by the moving average method.)
Equity securities for which market values are unavailable:
Cost method by the moving average method
(b) Derivatives…………………………… Fair value method
(c) Inventories……………………………. Cost method mainly by the gross average method (Figures on
the consolidated balance sheet are calculated by the method
of book devaluation based on the reduction of profitability.)
2)
Method of depreciation and amortization of significant depreciable assets
(a) Property, plant and equipment (excluding lease assets)
…………………… Mainly declining balance method
(b) Intangible assets (excluding lease assets)
…………………… Straight line method
(c) Lease assets
Finance leases which transfer ownership
…………………… The same method as depreciation and amortization of self-
owned noncurrent assets
Finance leases which do not transfer ownership
…………………… Straight-line method with the lease period as the durable
years. With regard to lease assets with guaranteed residual
value under lease agreement, remaining value is the
guaranteed residual value. And with regard to other lease
assets, remaining value would be zero.
3)
Accounting treatment for deferred assets
…………………… They are treated as expenses at the time of expenditure.
4)
Basis for significant allowances and provisions
(a) Allowance for doubtful accounts
In order to allow for loss from bad debts, estimated uncollectible amount based on actual
ratio of bad debt is appropriated as to general receivable. With regard to specific receivable
with higher default possibility, possibility of collection is estimated, respectively and
uncollectible amount is appropriated.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
4
(b) Allowance for investment loss
The differences between the book value and the fair value of equity securities for which
market values are unavailable are determined and appropriated as reserve in order to allow
for losses from these investments.
(c) Provision for product warranties
The provision is recorded into this account based on the warranty agreement, laws and
regulations and past experience in order to allow for expenses related to the maintenance
service of products sold.
(d) Provision for bonuses for directors
In order to pay bonuses for directors and audit & supervisory board members, estimated amount
of such bonuses is appropriated.
(e) Provision for retirement benefits for directors
The amount to be paid at the end of year had been posted pursuant to the Company’s
regulations on the retirement allowance of directors and audit & supervisory board members.
However, the Company’s retirement benefit system for them was abolished at the closure of the
ordinary general shareholders’ meeting held on June 29, 2006. And it was approved at the
shareholders’ meeting that reappointed directors and audit & supervisory board members were
paid their retirement benefit at the time of their retirement, based on their years of service.
Estimated amount of such retirement benefits is appropriated.
Furthermore, for the directors and audit & supervisory board members of some consolidated
subsidiaries, the amount to be paid at the end of the year was posted pursuant to their
regulation on the retirement allowance of directors and audit & supervisory board members.
(f) Provision for disaster
Reasonably estimated amount is appropriated for anticipated loss mainly caused by relocation
of plants and facilities located in the Ryuyo Region in Iwata City, Shizuoka Prefecture where
massive tsunami damages caused by Tokai and Tonankai Earthquake are anticipated.
(g) Provision for product liabilities
With regards to the products exported to North American market, to prepare for the payment of
compensation not covered by “Product Liability Insurance,” the anticipated amount to be borne
by the Company is computed and provided on the basis of actual results in the past.
(h) Provision for recycling expenses
The provision is appropriated for an estimated expenses related to the recycle of products of
the Company based on number of vehicles owned in the market, etc.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
5
5)
Recognition criteria for revenue and expenses
(a) Revenue
The Group is engaged in manufacturing and sale of automobiles, motorcycles, outboard
motors, electric wheelchairs, etc. in addition to the logistics services associated to these
businesses and other service businesses. The Group recognizes revenue from sale of the
above goods at the time when it satisfies a performance obligation by transferring control
of the goods or services to a customer in an amount that the Group expects to be entitled
in exchange for those goods and services.
Such amounts exclude the amount of consumption tax and value added tax levied on
behalf of tax authorities.
For contracted prices with customers, which include variable consideration, the Group
measures revenue less variable consideration only to the extent that it is highly probable
that there will be no significant reversal when the uncertainty associated with the variable
consideration is subsequently resolved.
Variable consideration mainly consists of sales rebates calculated based on past
transactions using the most likely amount method.
The Group recognizes revenue when it satisfies performance obligation over time or at a
point in time. As for the sale of automobiles, since the performance obligation is
considered fulfilled at the point in time when the products are delivered and the control of
such products is acquired by the customers, the revenue is recognized at the delivery of
the products.
If the Group provides services other than the warranty that the finished goods comply with
the agreed-upon specifications, such as a customer-paid extended warranty covering
longer than the standard period of time, revenue from such services is recognized over
the duration of the warranty in proportion to expenses to be incurred to satisfy
performance obligations under the contract.
The Group receives consideration mainly as advance payment during the period from the
time of receipt of a purchase order until the fulfillment of the performance obligation or
within one year after the fulfilment of the performance obligation. No significant financing
component is included in such transaction.
(b) Revenue recognition of finance lease transactions:
Net sales and costs of sales are recognized when due for payment of lease fees has
come.
6)
Accounting treatment pertaining to retirement benefits
(a) Method of attributing expected benefit to periods
With regard to calculation of retirement benefit obligations, benefit formula basis method
was used to attribute expected benefit to period up to the end of this fiscal year.
(b) Method to recognize actuarial gains or losses and past service costs as expenses
With regard to past service costs, they are treated as expense on a straight-line basis over
the certain years within the period of average length of employees’ remaining service years
at the time when it occurs.
With regard to the actuarial gains or losses, the amounts, prorated on a straight-line basis
over the certain years within the period of average length of employees’ remaining service
years in each year in which the differences occur, are respectively treated as expenses from
the next term of the year in which they arise.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
6
7)
Standards for translation of significant assets or liabilities in foreign currencies into the
Japanese currency
Receivable and payable in foreign currencies are translated into yen on the spot exchange rate of
the consolidated account settlement date, and the exchange difference shall be processed as gain
or loss. Further, assets and liabilities of foreign consolidated subsidiaries and others shall be
translated into yen by the spot exchange rate as of the consolidated account settlement date,
profits and expenses are translated into yen by the average exchange rate during the year, and
exchange differences shall be recorded to foreign currency translation adjustment and non–
controlling interests of the net assets.
8)
Method of significant hedge accounting
The deferred hedge processing is applied in principle.
9)
Other significant matters for preparing consolidated financial statements
The Company and certain of its domestic consolidated subsidiaries have applied the Group Tax
Sharing System. Accounting and disclosure for income taxes, local income taxes, and tax effect
accounting are in accordance with the “Treatment of Accounting and Disclosure under the Group
Tax Sharing System” (Practical Solution Report No. 42, August 12, 2021.)

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
7
2.
Notes to Accounting Estimates
(1)
Provision for product warranties
1)
Amount recorded in the consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
(Amount: Millions of yen)
End of the current
consolidated fiscal year
Balance at the beginning of the period
208,282
Amount paid during the period
(29,758)
Transferred amount
11,529
Balance at the end of the period
190,053
2)
Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
The Group recognizes provision for product warranties for costs related with future product
warranties.
Costs related to product warranty include (i) free repair costs based on the product warranty,
and (ii) free repair costs based on notification to a government agency. (i) Free repair costs
based on the product warranty are recognized at the time the product is sold. Regarding (ii) free
repair costs based on notifications to a government agency, if there is a high possibility that
costs will be incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated, the provision will be
recognized based on comprehensive and individual estimates based on past occurrences.
The amount of these provisions is estimated and calculated regarding the estimated number of
units and the cost per forecasted units based on currently available information, such as past
sales, repairs, and experience, and reflects the amount expected to be recovered by claiming
compensation from the supplier. Provision for product warranties contain uncertainties as it is
calculated by estimation. Therefore, the actual repair cost may differ from the estimate.
(2)
Retirement benefits asset and retirement benefits liability
1)
Amount recorded in the consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
Retirement benefits asset 19,241 Million Yen
Retirement benefits liability 59,894 Million Yen
2)
Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
The Group's retirement benefit expenses, retirement benefit asset and retirement benefits liability
are calculated based on various assumptions such as discount rate, expected rate of return on
long-term investment, revaluation rate, salary increase rate, mortality rate, etc. Of these, the
discount rate is determined based on safe long-term bond yields and the expected rate of return on
long-term investment is determined based on the pension asset management policy of each
pension plan.
The decline in long-term bond yields will reduce the discount rate and adversely affect the
calculation of retirement benefit costs. However, in the cash-balanced pension system adopted by
the Company, the revaluation rate, which is one of the basic rates, has the effect of reducing the
adverse effects of a decrease in the discount rate.
Additionally, if the investment yield of pension assets is lower than the expected rate of return on
long-term investment, it will adversely affect the calculation of retirement benefit costs, but the
impact on our corporate pension and the Group's corporate pension fund, which strive for stable
management, is minor.
The difference between these assumptions and the actual results is expensed mostly by the
straight-line method over a fixed number of years within the average remaining service period of
the employee at the time of occurrence.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
8
(3)
Deferred tax assets
1)
Amount recorded in the consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
Deferred tax assets 85,444 Million Yen
Deferred tax liabilities 4,114 Million Yen
2)
Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
We are examining whether the recoverability of deferred tax assets has an effect of reducing future
tax burdens, etc. for some or all of the deductible temporary differences, loss carryforwards and
tax credits carried forward.
The appraisal of recoverability of deferred tax assets takes into account elimination of taxable
temporary differences, estimation of future taxable income, and tax planning.
Regarding this estimate, in the event of a changes in future market trends, business activity
status, or other assumptions related to the Group, it may affect the amount of deferred tax assets
and income taxes–deferred from the next fiscal year onward.
3.
Notes to Consolidated Balance Sheets
(1)
Assets pledged as collateral and secured liabilities
1)
Assets pledged as collateral
Machinery and equipment 814 Million Yen
2)
Secured liabilities
Long-term borrowings 734 Million Yen
(2)
Accumulated depreciation of property, plant and equipment 2,597,890 Million Yen
(3)
Guarantee obligations
The Group guarantees borrowing from financial institution etc. by other companies which are
not consolidated subsidiaries.
2,212 Million Yen
(4)
The Company has the commitment line contract with 6 banks for effective financing.
The outstanding balance of the contract at the end of the current consolidated fiscal year is as follows.
Commitment line contract total 300,000 Million Yen
Actual loan balance –
Undrawn balance 300,000 Million Yen
4.
Notes to Consolidated Statements of Income
Revenue from contracts with customers
The Company does not disaggregate revenues from contracts with customers and other revenue. The
amount of revenue from contracts with customers is presented in “7. Notes to Revenue Recognition,
(1) Breakdown of revenue from contracts with customers” in Notes to Consolidated Financial
Statements.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
9
5.
Notes to Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets
(1)
Type and number of outstanding shares
(Shares)
Type of shares
Number of shares at
the beginning of
current fiscal year
Increased number
of shares during the
period
Decreased number
of shares during the
period
Number of shares at
the end of current
fiscal year
Common stock
491,146,600
–
–
491,146,600
[Notes] A four–for-one common stock split was conducted on April 1, 2024; however, the items
listed above are based on the number of shares held before the split.
(2)
Dividends
1)
Dividends paid
Resolution
Type of shares
Total amount
of dividends
Dividends per
share
Record date
Effective date
Ordinary general
shareholders’
meeting held on
June 23, 2023
Common stock
24,305
Million Yen
50.00 Yen
March 31,
2023
June 26,
2023
Meeting of the
Board of Directors
held on
November 7, 2023
Common stock
26,530
Million Yen
55.00 Yen
September
30, 2023
November 30,
2023
2)
Dividends, which record date is during the current consolidated fiscal year, with their effective
date in the next consolidated fiscal year
The following dividends are proposed as a matter of resolution at the ordinary general
shareholders’ meeting scheduled to be held on June 27, 2024.
(a) Total amount of dividends 32,319 Million Yen
(b) Dividends per share 67.00 Yen
(c) Record date March 31, 2024
(d) Effective date June 28, 2024
Dividends will be paid from retained earnings.
[Notes] A four–for-one common stock split was conducted on April 1, 2024; however, the items
listed above are based on the number of shares held before the split.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
10
6.
Notes to Financial Instruments
(1)
Matters for conditions of financial instruments
With regard to the fund management, the Group uses short-term deposits and securities, and with
regard to the fund-raising, the Group uses borrowings from financial institutions such as banks and
issuance of bonds.
The Group mitigates customers’ credit risks from notes and accounts receivable-trade in line with
our rules and regulations for credit control. The Group hedges risks of exchange-rate fluctuations
from operating receivables denominated in foreign currency by forward exchange contract in
principle. Investment securities are mainly stocks and mutual funds, and with regard to listed
stocks and mutual funds, the Group quarterly identifies those fair values.
Applications of borrowings are operating capital (mainly short term) and fund for capital
expenditures (long term). The Group uses cross currency interest rate swap as hedge instruments
for the risk of fluctuation in interest rate and foreign exchange rate of some long-term borrowings.
In addition, the Group uses derivatives within the actual demand in accordance with our
administrative rules.
(2)
Matters for fair values of the financial instruments
Carrying amounts in the consolidated balance sheet, fair value and differences between them at
March 31, 2024 (consolidated settlement date of current fiscal year) are as follows.
“Cash and deposits,” “Accounts payable-trade,” “Short-term borrowings,” and “Accrued
expenses” are omitted because they comprise cash and are short-term instruments whose
carrying amount approximates their fair value.
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Carrying
amount
Fair value
Difference
Assets
(a) Notes and accounts receivable-trade
565,011
559,746
(5,265)
(b) Securities and investment securities (*1, *2)
Available-for-sale securities
1,377,620
1,377,620
–
Stocks of associates
1,336
3,271
1,935
Total assets
1,943,968
1,940,637
(3,330)
Liabilities
Long-term borrowings
619,638
617,094
2,544
Total liabilities (*3)
619,638
617,094
2,544
Derivatives (*4)
(3,727)
(3,727)
–
[Notes] 1. Equity securities for which market values are unavailable are not included in the above
(b) Securities and investment securities.
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Account Title
Carrying Amount
Available-for-sale securities
Unlisted stocks other than stocks of
associates
27,216
Unlisted stocks of associates
65,110
2.
Notes on investments in partnerships and other similar entities for which equity interests
are recorded on a net basis on the consolidated balance sheet are omitted. The amount of
these investments recorded on the consolidated balance sheet is 32,368 million yen.
3.
Total liabilities include current portion of long-term borrowings.
4.
Assets or liabilities derived from derivatives are shown on a net basis and net liabilities are
shown as ( ).

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
11
(3)
Fair value information by level within the fair value hierarchy
The fair value of financial instruments is classified into the following three levels according to the
observability and significance of inputs used to measure fair value.
Level 1 fair value: Fair value measured using quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets
for the same assets or liabilities.
Level 2 fair value: Fair value measured using directly or indirectly observable inputs other
than Level 1 inputs.
Level 3 fair value: Fair value measured using significant unobservable inputs.
If multiple inputs are used that are significant to the fair value measurement, the fair value
measurement is categorized in its entirety in the level of the lowest level input that is significant
to the entire measurement.
1) Financial assets and financial liabilities measured at fair value
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Category
Fair value
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Total
Securities and investment securities
Available-for-sale securities
Stocks
295,628
–
–
295,628
Bonds
–
75,106
–
75,106
Mutual funds
968,864
6,928
1,092
976,885
Others
–
30,000
–
30,000
Total assets
1,264,493
112,034
1,092
1,377,620
Derivatives
–
(3,727)
–
(3,727)
2) Financial assets and financial liabilities not measured at fair value
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Category
Fair value
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Total
Accounts receivable-trade
–
559,746
–
559,746
Securities and investment securities
Stocks of associates
3,271
–
–
3,271
Total assets
3,271
559,746
–
563,017
Long-term borrowings
–
617,094
–
617,094
Total liabilities
–
617,094
–
617,094

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
12
[Notes] 1. Description of the valuation techniques and inputs used in the fair value measurement
Assets
Accounts receivable-trade
The fair value of these items is measured using the discounted cash flow method
based on the amount of receivables, period to maturity and an interest rate reflecting
credit risk, for each receivable categorized by a specified period, and is classified as
Level 2.
Securities and investment securities
Listed shares and bonds are valued using quoted prices. As listed shares are traded in
active markets, their fair value is classified as Level 1. On the other hand, the fair value
of bonds held by the Company are classified as Level 2 because they are not traded
frequently in the public market and not considered to have quoted prices in active
markets. In addition, beneficiary certificates of mutual funds whose market value is
the price presented by a third party are classified into Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3
based on the obtained price and the observability in the inputs used for pricing.
Liabilities
Long-term borrowings
The fair value of these items is measured using the discounted cash flow method
based on the sum of principal and interest, remaining maturities and an interest rate
reflecting credit risk, and is classified as Level 2.
Derivatives transactions
The fair value of cross currency interest rate swaps and forward exchange contracts is
measured using the discounted cash flow method based on observable inputs, such as
interest rates and exchange rates, and is classified as Level 2.
2. Assets or liabilities derived from derivatives are shown on a net basis and net
liabilities are shown as ( ).
3. Information on fair values of Level 3 financial assets and financial liabilities with
the carrying amount not recorded using the fair value
Note is omitted because it is insignificant.
7.
Notes to Revenue Recognition
(1)
Breakdown of revenue from contracts with customers
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Automobiles
Business
Motorcycles
Business
Marine
Business
Other
Business
Total
Japan
1,253,124
19,765
3,357
11,235
1,287,482
Europe
634,531
46,876
18,933
–
700,341
Asia
2,393,389
185,142
13,829
–
2,592,360
Others
574,133
114,797
76,157
–
765,089
Revenue from
contracts with
customers
4,855,179
366,581
112,278
11,235
5,345,274
Other revenue
[Note] 2
28,624
353
3
–
28,981
Net sales to
external
customers
4,883,804
366,934
112,281
11,235
5,374,255
[Notes] 1. Revenue is disaggregated by region based on the location of customers.
2. Other revenue includes income from lessor lease, etc.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
13
(2)
Basic information for understanding revenue
The details are the same as described in “1. Notes to Basic Significant Matters for Preparing
Consolidated Financial Statements (4) Accounting Policy 5) Recognition criteria for revenue
and expenses” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
(3)
Basic information for understanding the revenue amounts in the current and next fiscal years
1)
Receivables from contracts with customers and contract liabilities
Receivables from contracts with customers and contract liabilities in the current fiscal year are as
follows:
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Balance at the end
of
the period
Receivables from contracts with
customers
529,699
Notes receivable-trade
949
Accounts receivables-trade
528,750
Contract liabilities
177,932
Other current liabilities
120,074
Other non-current liabilities
57,858
Contract liabilities are mainly consideration received from customers prior to delivery of the product. Of the
revenue recognized in the current fiscal year, the amount included in the contract liability balance as of the
beginning of the period was 92,985 million yen. The amount of revenue recognized from performance
obligations fulfilled (or partially fulfilled) in the past period is not significant.
2)
Transaction price allocated to the remaining performance obligations
The Company and consolidated subsidiaries have applied the practical expedient to the notes
on transaction prices allocated to the remaining performance obligations, and does not disclose
contracts with an original expected duration of one year or less. Consideration arising from
contracts with customers does not have any significant amounts not included in the transaction
price.
As of the end of the current fiscal year, the total transaction price allocated to unfulfilled
performance obligations and the period during which revenue is expected to be recognized are
as follows:
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Current fiscal year
Within one year
42,883
Over one year
67,107
Total
109,991
Remaining performance obligations consist primarily of extended warranty income and
maintenance income.
8.
Notes to Information about Per Share Amount
Net assets per share 1,291.25 Yen
Profit per share, Basic 138.40 Yen
[Notes] A four–for-one common stock split was conducted on April 1, 2024.
Net assets per share and profit per share, basic are calculated on the assumption that the stock
split was conducted at the beginning of this consolidated fiscal year.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
14
9.
Notes to Significant Subsequent Events
(Stock split and Related Amendment to the Articles of Incorporation)
The Company conducted stock split and partially amended its Articles of Incorporation on April 1, 2024 based on
a resolution of the Board of Directors meeting held on December 13, 2023.
(1)
Stock Split
1)
Purpose of the Stock Split
The purpose is to lower the minimum investment amount through the stock split, thereby creating
an environment where it is easier to invest in the Company’s shares and expanding the Company’s
investor base.
2)
Outline of the Stock Split
(a) Stock Split Method
The record date for the stock split was Sunday, March 31, 2024. Since this day falls on a
non-business day of the shareholder registry administrator, the substantial record date
was Friday, March 29, 2024. Each share of the Company’s common stock held by
shareholders as of the record date was split into 4 shares.
(b) Increase in Number of Shares as a Result of the Stock Split
Total number of issued shares before the stock split
491,146,600 shares
Increase in number of shares due to the stock split
1,473,439,800 shares
Total number of issued shares after the stock split
1,964,586,400 shares
Total number of issuable shares after the stock split
6,000,000,000 shares
(c) Stock Split Schedule
Public notice of record date
Friday, March 15, 2024
Record date
Sunday, March 31, 2024
Effective date
Monday, April 1, 2024
3)
Impact for information of per share
The impact of the stock split is described in the relevant section.
(2)
Partial Amendment to Articles of Incorporation
1)
Reason for Amendment
Due to the stock split described above, the Company partially amended its Articles of Incorporation,
effective as of Monday, April 1, 2024, pursuant to Article 184, Paragraph 2 of the Companies Act.
2)
Details of Amendment to Articles of Incorporation
The details of the amendment are as follows: (Underlined part indicates amendment)
Articles of Incorporation before Amendment
After Amendment
(Total Number of Issuable Shares)
Article 6.
The total number of the Company’s issuable
shares shall be 1,500,000,000 shares.
(Total Number of Issuable Shares)
Article 6.
The total number of the Company’s issuable
shares shall be 6,000,000,000 shares.
3)
Schedule of Amendments to the Articles of Incorporation
Effective Date: Monday, April 1, 2024
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
15
10.
Other Notes
(Business Combinations)
Transaction under common control, etc.
(1)
Outline of the Transaction
1)
Name of the acquired company and its business
Maruti Suzuki India Limited ("MSIL") Production and Sale of products of the Company
Suzuki Motor Gujarat ("SMG") Production of products of the Company
2)
Date of business combination
November 24, 2023 (Deemed date of acquisition: December 31, 2023)
3)
Legal form of the business combinations
In relation to change of SMG, an Indian subsidiary, to a sub-subsidiary, the Company transferred all of the
shares of SMG held by the Company to MSIL, and subscribed shares issued by MSIL on a preferential
allotment basis as consideration for the transfer.
4)
Name of the company after the business combination
No change
5)
Other matters on the outline of the transaction
The purpose of this transaction was to further enhance competitiveness through streamlining production
operations by MSIL’s controlling production of automobiles in India.
The ratio of shares held by the Company in MSIL became 58.19% from 56.48% before the capital increase.
(2)
Outline of Accounting treatment applied
In accordance with the Accounting Standard for Business Combinations (ASBJ Statement No. 21, January 16,
2019) and the Implementation Guidance on Accounting Standard for Business Combinations and Accounting
Standard for Business Divestitures (ASBJ Guidance No. 10, January 16, 2019), the transaction is treated as a
transaction under common control.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
16
Non-Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets (April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024)
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Shareholders' equity
Share capital
Capital surplus
Retained earnings
Legal capital
surplus
Other capital
surplus
Total capital
surplus
Legal retained
earnings
Other retained
earnings
Reserve for
tax purpose
reduction
entry of
non-current
assets
Balance at the beginning of
current fiscal year
138,370
144,720
1,568
146,289
8,269
12,841
Changes during period
Provision of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
4,743
Reversal of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
(4,641)
Provision of reserve for
promoting open innovation
Provision of general reserve
Dividends of surplus
Profit
Purchase of treasury shares
Disposal of treasury shares
42
42
Net changes in items other
than shareholders' equity
Total changes during period
–
–
42
42
–
101
Balance at the end of current
fiscal year
138,370
144,720
1,611
146,331
8,269
12,942
Shareholders' equity
Retained earnings
Treasury
shares
Total
shareholders'
equity
Other retained earnings
Total retained
earnings
Reserve for
promoting open
innovation
General
reserve
Retained
earnings brought
forward
Balance at the beginning of
current fiscal year
–
458,000
143,480
622,592
(19,331)
887,920
Changes during period
Provision of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
(4,743)
–
–
Reversal of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
4,641
–
–
Provision of reserve for
promoting open innovation
412
(412)
–
–
Provision of general reserve
94,000
(94,000)
–
–
Dividends of surplus
(50,836)
(50,836)
(50,836)
Profit
203,112
203,112
203,112
Purchase of treasury shares
(20,004)
(20,004)
Disposal of treasury shares
125
168
Net changes in items other
than shareholders' equity
Total changes during period
412
94,000
57,761
152,275
(19,878)
132,439
Balance at the end of current
fiscal year
412
552,000
201,242
774,867
(39,209)
1,020,359

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
17
(Amount: Millions of yen)
Valuation and translation adjustments
Share acquisition
rights
Total net assets
Valuation difference
on Available-for-
sale securities
Deferred gains or
losses on hedges
Total valuation and
translation adjustments
Balance at the beginning of
current fiscal year
44,850
69
44,920
41
932,882
Changes during period
Provision of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
–
Reversal of reserve for tax
purpose reduction entry of
non-current asset
–
Provision of reserve for
promoting open innovation
Provision of general reserve
–
Dividends of surplus
(50,836)
Profit
203,112
Purchase of treasury shares
(20,004)
Disposal of treasury shares
168
Net changes in items other
than shareholders' equity
81,323
(156)
81,167
–
81,167
Total changes during period
81,323
(156)
81,167
–
213,606
Balance at the end of current
fiscal year
126,173
(86)
126,087
41
1,146,488
[Note] Amounts less than one million yen are rounded down.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
18
Notes to Non-Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Notes to Significant Accounting Policies
(1)
Evaluation standards and evaluation methods of assets
1) Securities
Stocks of subsidiaries and associates……… Cost method by the moving average method
Other securities of affiliated companies… Investments in partnerships like Investment
Limited Partnership (which are regarded as securities
under Article 2–2 of the Financial Instruments and
Exchange Act) are recorded on a net basis equivalent
to the equity interest based on the most recent
financial statements available on the reporting date
stipulated in the contract.
Available-for-sale securities…………………… Items other than equity securities for which market
values are unavailable:
Fair value method (The evaluation differences shall be
reported as a component of net assets, and costs of
securities sold shall be calculated by the moving
average method)
Equity securities for which market values are
unavailable:
Cost method by the moving average method
2) Derivatives .............................................….. Fair value method
3) Inventories ...........................................….... Cost method mainly by the gross average method
(figures on the balance sheet are calculated by the
method of book devaluation based on the reduction of
profitability.)
(2)
Method of depreciation and amortization of non-current assets
1) Property, plant and equipment (excluding lease assets)
………………… Declining-balance method
2) Intangible assets (excluding lease assets)
………………… Straight-line method
3) Lease assets
Finance leases which transfer ownership
………………… The same method as depreciation and amortization of
self-owned non-current assets
Finance leases which do not transfer ownership
………………… Straight-line method with the lease period as the
durable years. With regard to lease assets with
guaranteed residual value under lease agreement,
remaining value is the guaranteed residual value. And
with regard to other lease assets, remaining value
would be zero.
(3)
Accounting treatment for deferred assets
………………… They are treated as expenses at the time of
expenditure.
(4)
Allowances and provisions
1) Allowance for doubtful accounts
In order to allow for loss from bad debts, estimated uncollectible amount based on actual ratio
of bad debt is appropriated as to general receivable. With regard to specific receivable with
higher default possibility, possibility of collection is estimated respectively and estimated
uncollectible amount is appropriated.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
19
2) Allowance for investment loss
The differences between the book value and the fair value of equity securities for which
market values are unavailable are determined and appropriated as reserve in order to allow for
losses from these investments.
3) Provision for product warranties
The provision is appropriated into this account based on the warranty agreement, laws and
past experience in order to allow for expenses related to the maintenance service of products
sold.
4) Provision for retirement benefits
In order to allow for payment of employees’ retirement benefits, provision is recognized based
on estimated amount of retirement benefits liabilities and pension assets at the end of current
fiscal year is appropriated.
(a) Method of attributing expected benefit to periods
With regard to calculation of retirement benefit liability, benefit formula basis method was
used to attribute expected benefit to period up to the end of this fiscal year.
(b) Method to recognize actuarial gains or losses and past service costs as expenses
With regard to past service costs, they are treated as expense on a straight line basis over
the certain years within the period of average length of employees’ remaining service years
at the time when it occurs.
With regard to the actuarial gains or losses, the amounts, prorated on a straight-line basis
over the certain years within the period of average length of employees’ remaining service
years in each year in which the differences occur, are respectively treated as expenses
from the next term of the year in which they arise.
5) Provision for retirement benefits for directors
The amount to be paid at the end of year had been posted pursuant to the Company’s
regulations on the retirement allowance of directors and audit & supervisory board members.
However, the Company’s retirement benefit system for them was abolished at the closure of
the ordinary general shareholders’ meeting held on June 29, 2006. And it was approved at the
shareholders’ meeting that reappointed directors and audit & supervisory board members were
paid their retirement benefit at the time of their retirement, based on their years of service.
Estimated amount of such retirement benefits is appropriated.
6) Provision for product liabilities
With regards to the products exported to North American market, to prepare for the payment
of compensation not covered by “Product Liability Insurance,” the anticipated amount to be
borne by the Company is computed and provided on the basis of actual results in the past.
7) Provision for recycling expenses
The provision is recorded for an estimated expense related to the recycle of products of the
Company based on number of vehicles owned in the market, etc.
(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
20
(5)
Recognition criteria for revenue and expenses
The Company is engaged in manufacturing and sale of automobiles, motorcycles, outboard motors,
electric wheelchairs, etc. in addition to the logistics services associated to these businesses and
other service businesses. The Company recognizes revenue from sale of the above goods at the
time when it satisfies a performance obligation by transferring control of the goods or services to
a customer in an amount that the Group expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods and
services.
Such amounts exclude the amount of consumption tax and value added tax levied on behalf of tax
authorities.
For contracted prices with customers, which include the variable consideration, the Company
measures the revenue less variable consideration only to the extent that it is highly probable that
there will be no significant reversal when the uncertainty associated with the variable
consideration is subsequently resolved.
Variable consideration mainly consists of sales rebates calculated based on past transactions using
the most likely amount method.
The Company recognizes revenue from sale of automobiles when it satisfies performance
obligation mainly at a point in time. As for the sale of automobiles, since the performance
obligation is considered fulfilled at the point in time when the products are delivered and the
control of such products is acquired by the customers, the revenue is recognized at the delivery of
the products.
The Company receives consideration mainly as advance payment during the period from the time
of receipt of a purchase order until the fulfillment of the performance obligation or within one year
after the fulfilment of the performance obligation. No significant financing component is included
in such transaction.
(6)
Standards for translation of significant assets and liabilities in foreign currencies into the Japanese
currency
Receivable and payable in foreign currencies are translated into yen on the spot exchange rate of the
account settlement date, and the translation difference shall be processed as gain or loss.
(7)
Method of hedge accounting
The deferred hedge processing is applied in principle.
(8)
Other significant matters for preparing financial statements
Application of group tax sharing system
The group tax sharing system is applied.

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
21
2. Notes to Accounting Estimates
(1)
Provision for product warranties
1) Amount recorded in the Non-Consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
(Amount: Millions of yen)
End of the current fiscal year
Balance at the beginning of the period
196,447
Amount paid during the period
(29,740)
Transferred amount
10,327
Balance at the end of the period
177,034
2) Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
The details are the same as described in “2. Notes to Accounting Estimates (1) Provision for
product warranties” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
(2)
Prepaid pension costs and provision for retirement benefits
1) Amount recorded in the Non-Consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
Prepaid pension costs 30,474 Million Yen
Provision for retirement benefits 22,510 Million Yen
2) Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
The details are the same as described in “2. Notes to Accounting Estimates (2) Retirement
benefits asset and retirement benefits liability” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial
Statements.
(3)
Deferred tax assets
1) Amount recorded in the Non-Consolidated financial statements for the current fiscal year
Deferred tax assets 96,383 Million Yen
2) Information regarding the details of the accounting estimate for the identified item
The details are the same as described in “2. Notes to Accounting Estimates (3) Deferred tax
assets” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
3. Notes to Non-Consolidated Balance Sheets
(1)
Monetary receivables from and payables to subsidiaries and associates
Short-term receivables 376,482 Million Yen
Short-term payables 325,394 Million Yen
(2)
Accumulated depreciation of property, plant and equipment 927,401 Million Yen
(3)
Guarantee obligations
The Company guarantees the other companies’ borrowings from financial institutions.
Suzuki Thilawa Motor Co., Ltd. 4,466 Million Yen
Other 299 Million Yen
Total 4,766 Million Yen
(4)
The Company has the commitment line contract with 6 banks for effective financing.
The outstanding balance of the contract at the end of current fiscal year is as follows.
Commitment line contract total 300,000 Million Yen
Actual loan balance –
Undrawn balance 300,000 Million Yen

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
22
4. Notes to Non-Consolidated Statements of Income
Amount of transactions with subsidiaries and associates
Amount of net sales 1,949,541 Million Yen
Amount of purchase 658,815 Million Yen
Amount of other operating transactions 120,525 Million Yen
Amount of transactions other than operating transactions 69,447 Million Yen
5. Notes to Non-Consolidated Statement of Changes in Net Assets
Type and number of treasury shares
(Shares)
Type of shares
Number of shares
at the beginning of
current fiscal year
Increased number
of shares during the
period
Decreased number
of shares during the
period
Number of shares
at the end of
current fiscal year
Common stock
5,031,544
3,768,383
31,200
8,768,727
[Notes] 1. The increase of 3,768,383 shares in treasury shares of common stock consists of purchase of 3,767,600
shares in treasury shares based on resolution of board of directors’ meeting s and purchase of 783
shares in odd stocks.
2. The decrease of 31,200 shares in treasury shares of common stocks consists of restricted stock
compensation.
3. A four–for-one common stock split was conducted on April 1, 2024. However, the above items are based
on the number of shares prior to the stock split.
6. Notes to Tax Effect Accounting
(1)
Breakdown of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities by their main occurrence
causes
(Deferred tax assets) (Millions of yen)
Impairment losses and excess
depreciation
47,501
Various reserves
67,089
Loss on valuation of securities
50,509
Others
64,735
Sub–total deferred tax assets
229,835
Valuation reserve
(65,123)
Total deferred tax assets
164,712
(Deferred tax liabilities)
Valuation difference on available-for-sale
securities
(53,714)
Prepaid pension costs
(9,099)
Others
(5,514)
Total deferred tax liabilities
(68,328)
Deferred tax assets, net
96,383

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
23
(2)
Details of differences which cause important differences between statutory tax rate and the
effective tax rate after application of tax effect accounting
Statutory tax rate
(Adjustment)
29.9 %
Valuation reserve
3.9 %
Tax credit
(8.4)%
Tax-deductible of dividend income
(5.5)%
Others
1.8 %
Effective tax rate after application of tax
effect accounting
21.6 %
(3)
Application of Accounting treatment and disclosure in the case of applying the Group Tax Sharing
System
The Company have applied the Group Tax Sharing System. Accounting and disclosure for income taxes, local
income taxes, and tax effect accounting are in accordance with the “Treatment of Accounting and Disclosure
under the Group Tax Sharing System” (Practical Solution Report No. 42, August 12, 2021.)

(This is an English translation of the original document in Japanese language provided on our website and is for reference purpose only.
If there are any discrepancies between this document and original Japanese one, the original prevails.)
24
7. Notes to Related Party Transactions
Subsidiaries and associates, etc.
Type
Name
Own
(owned)
voting right
(%)
Relation with related
parties
Details of
transaction
[Note] 1
Amounts of
transaction
(Million Yen)
Account
Balance at
the end of
current fiscal
year
(Million Yen)
Subsidiary
Suzuki Finance
Co., Ltd.
Owning
direct
95.9
Financial services
related to sale of
products of the
Company
Loan transaction.
Concurrent post of
Directors/Company
auditors
Collection of
credit
47,751
Other
current
assets
50,899
Subsidiary
Suzuki Motor
de Mexico S.A.
de C.V.
Owning
direct
100.0
Indirect
0.0
Sale of products of the
Company
Sale of
products
111,672
Accounts
receivable-
trade
42,950
Subsidiary
Maruti Suzuki
India Ltd.
Owning
direct
58.2
Manufacture and sale of
products of the
Company
Concurrent post of
Directors/Company
Auditors
Sale of
products
142,677
Accounts
receivable-
trade
48,383
Subscription
of increased
shares
(Note) 3
204,090
–
–
Subsidiary
Magyar Suzuki
Corporation
Ltd.
Owning
direct
97.5
Manufacture and sale of
products of the
Company
Purchase of
products
308,142
Accounts
payable-
trade
11,710
Subsidiary
Suzuki
Deutschland
GmbH
Owning
direct
100.0
Sale of products of the
Company
Receiving
deposits of
funds
[Note] 2
37,928
Deposits
received
32,796
[Notes] 1. Conditions of transaction are determined taking into consideration arms-length basis based on market prices.
2. The interest rates of deposits are determined by taking the market interest rate into consideration. The
transaction amounts are the average balance during the period.
3. The Company subscribed all amount of the third-party allotment conducted by Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. See the
details of the transaction in “10. Other Notes (Business Combinations)” in Notes to Consolidated Financial
Statements.
8. Notes to Information about Per Share Amount
Net assets per share 594.16 Yen
Profit per share, Basic 104.98 Yen
[Notes] A four–for-one common stock split was conducted on April 1, 2024.
Net assets per share and profit per share, basic are calculated on the assumption that the stock
split was conducted at the beginning of the previous fiscal year.
9. Notes on Significant Subsequent Events
This information is omitted because it appears in the “9. Notes to Significant Subsequent Events” section of the
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
