
: COMPUTING FUNDAMENTALS, CERT
In Workflow
4. KP Dean ([email protected])
5. University Librarian ([email protected])
7. Provost ([email protected])
9. Senate ([email protected])
10. U Senate Conf (none)
11. Board of Trustees (none)
12. IBHE (none)
Approval Path
1. Thu, 04 Feb 2021 17:30:28 GMT
Deb Forgacs (dforgacs): Approved for U Program Review
2. Fri, 05 Feb 2021 00:11:39 GMT
Elsa Gunter (egunter): Approved for 1434 Head
3. Tue, 23 Mar 2021 18:59:16 GMT
Keri Pipkins (kcp): Approved for KP Committee Chair
4. Tue, 23 Mar 2021 19:03:30 GMT
Candy Deaville (candyd): Approved for KP Dean
5. Tue, 23 Mar 2021 19:09:21 GMT
John Wilkin (jpwilkin): Approved for University Librarian
6. Thu, 01 Apr 2021 20:04:52 GMT
Allison McKinney (agrindly): Approved for Grad_College
7. Thu, 01 Apr 2021 21:23:59 GMT
Kathy Martensen (kmartens): Approved for Provost
New Proposal
Date Submitted:Tue, 02 Feb 2021 22:58:36 GMT
Viewing:: Computing Fundamentals, CERT
Changes proposed by: Viveka Kudaligama
Proposal Type
Proposal Type:
Major (ex. Special Education)
Proposal Title:
If this proposal is one piece of a multi-element change please include the other impacted programs here.example: A BS revision with multiple
concentration revisions
Establish a Campus Graduate Certificate in Computer Science
EP.21.105_FINAL
Approved by EP 04/12/2021
APPROVED BY SENATE
04/26/2021

EP Control Number
EP.21.105
Official Program Name
Computing Fundamentals, CERT
Effective Catalog Term
Fall 2021
Sponsor College
Grainger College of Engineering
Sponsor Department
Computer Science
Sponsor Name
Nancy Amato
Sponsor Email
College Contact
Harry Dankowicz, Associate Dean for Graduate, Professional, and Online Programs
College Contact Email
Program Description and Justification
Provide abriefdescription and justification of the program, including highlights of the program objectives, and the careers, occupations, or further
educational opportunities for which the program will prepare graduates, when appropriate.
The proposed Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals prepares students who have a Bachelors (or higher) degree, but not in computing, to
transition into computing careers in industry or graduate studies in computer science. The Certificate consists of an onramp (or bridging courses)
in programming, data structures, and algorithms. To prepare for the transition to industry or graduate studies, students complete an independent
study project and a graduate-level elective. In addition, excursions seminars provide students with breadth in computing through engaging with guest
speakers, reading scientific papers, and interacting with core computing tools.
The proposed Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals consists of 20 credit hours, where up to 8 credit hours transfer to graduate degree
programs (Masters program codes 1SKS0112MCSU, 10KS0112MCS, 10KS0112MS, 10KS4028MS; PhD program code 10KS0112PHD) in CS. The 8
credit hours of transferrable coursework may not include the bridging courses: CS 400, CS 401, CS 402, and CS 403.
The proposed Certificate will be offered as part of the iCAN (Illinois Computing Accelerator for Non-specialists) program.
https://cs.illinois.edu/academics/graduate/ican

Corresponding Degree
CERT Campus Graduate Certificate
Is this program interdisciplinary?
No
Academic Level
Graduate
Will you admit to the concentration directly?
No
Is a concentration required for graduation?
No
CIP Code
11.0701 - 11.0701
Is This a Teacher Certification Program?
No
Will specialized accreditation be sought for this program?
No
Institutional Context
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Describe the historical and university context of the program's development. Include a short summary of any existing program(s) upon which this
program will be built.
Explain the nature and degree of overlap with existing programs and, if such overlap exists, document consultation with the impacted program’s home
department(s).
This is a new program that does not build upon any existing program. There is no overlap of this program with any existing program.
University of Illinois

Briefly describe how this program will support the University's mission, focus and/or current priorities. Demonstrate the program's consistency with
and centrality to that mission.
The mission of the University and the CS department is to provide an education in computing to society at large. Unfortunately, the population makeup
of undergraduate students in CS (and more generally STEM disciplines) is not representative of the demographics of Illinois. This results in a skewed
representation at the graduate level and the computing industry as well. Although there is a high demand for employees in the computing field, entry
into the field is difficult. The proposed Certificate program provides a strong foundation in computing fundamentals to postbaccalaureate students
without a computing background so that they can enter the computing field. It is especially designed with such students in mind by building on their
broad set of transferable skills (e.g., problem solving, creativity, dealing with complexity, focus) and on the knowledge such individuals bring from their
respective fields. Additionally, this program’s aim is to broaden participation in computing by forming a cohort whose demographics align with the
state of Illinois.
State of Illinois
Indicate which of the following goals of the Illinois Board of Higher Education's Strategic Initiative are supported by this program: (choose all that
apply)
High Quality Credentials to Meet Economic Demand - Increase the number of high-quality post-secondary credentials to meet the demands of the
economy and an increasingly global society.
Integration of Educational, Research and Innovation Assets - Better integrate Illinois' educational, research and innovation assets to meet economic
needs of the state and its regions.
Describe how the proposed program supports these goals.
There is a high demand for employees in the computing field, but entry into the field is difficult. As a result, there are not enough CS graduates to fill
the high demand. The proposed Certificate program fills this gap by providing a pathway for non-computing college graduates to gain the skills and
training necessary to enter into the computing industry or our top CS graduate program at Illinois.
Admission Requirements
Desired Effective Admissions Term
Fall 2021
Provide a brief narrative description of the admission requirements for this program. Where relevant, include information about licensure
requirements, student background checks, GRE and TOEFL scores, and admission requirements for transfer students.
The admission requirements for this program include a bachelor’s degree in a non-computing background from a regionally accredited college in the
United States or a comparable degree from a recognized institution of higher learning abroad and English proficiency. The criteria for admissions
rely upon two main parts: the application (academic transcripts, reference letters, resume, and short essays) and an interview (problem-solving
assessment). The admission process for the proposed Certificate is a holistic evaluation of the applicant.
Describe how critical academic functions such as admissions and student advising are managed.
The Program Director will provide oversight to professional staff with additional support from program faculty, to manage the admissions process and
student advising. The CS department has received approval to hire a program coordinator, but interim staff support is available in the department.
Enrollment
Number of Students in Program (estimate)

Year One Estimate
20
5th Year Estimate (or when fully implemented)
200
Estimated Annual Number of Degrees Awarded
Year One Estimate
20
5th Year Estimate (or when fully implemented)
200
What is the matriculation term for this program?
Fall
What is the typical time to completion of this program?
2 years
What are the minimum Total Credit Hours required for this program?
20
Delivery Method
This program is available:
On Campus and Online
Describe the use of this delivery method:
The program will be delivered on-campus and online. Online delivery will be offered in a synchronous or asynchronous format through
videoconferencing technology such as Zoom and will utilize learning management systems such as Compass to disseminate materials, post
videos, etc. CS department requests two dedicated program codes to differentiate the on-campus program and the online program. Program code
10KS0112NDEG currently in use at the department for the iCAN program. This can be repurposed for the on-campus program. A new program code
will be required for the online program.
Budget
Will the program or revision require staffing (faculty, advisors, etc.) beyond what is currently available?
Yes

Please explain/describe:
The program will require a program coordinator. This position has been requested and approved. We expect to fill it in spring 2021.
Additional Budget Information
We do not foresee any major impact on faculty hiring in the near term. The courses are already being offered and enrollments are expected to increase
as a result of the proposed Certificate. Additional enrollment may require the expenditure for additional Teaching Assistants to help staff discussion
sections, computing labs and office hours of CS core courses. These additional expenditures should be offset by the increase in revenue from the
tuition to the instructional unit.
Resource Implications
Facilities
Will the program require new or additional facilities or significant improvements to already existing facilities?
No
Technology
Will the program need additional technology beyond what is currently available for the unit?
No
Non-Technical Resources
Will the program require additional supplies, services or equipment (non-technical)?
No
Resources
For each of these items, be sure to include in the response if the proposed new program or change will result in replacement of another program(s).
If so, which program(s), what is the anticipated impact on faculty, students, and instructional resources? Please attach any letters of support/
acknowledgement from faculty, students, and/or other impacted units as appropriate.
Faculty Resources
Please address the impact on faculty resources including any changes in numbers of faculty, class size, teaching loads, student-faculty ratios, etc.
Describe how the unit will support student advising, including job placement and/or admission to advanced studies.
We currently have two faculty dedicated to teaching classes in this program. If the enrollment increases beyond the capacity of two faculty members,
additional faculty will be hired. Thus, this Certificate program will not impact faculty resources, class sizes, or teaching loads. We will need a program
coordinator, and this position has been requested and approved. We expect to fill the position in spring 2021.

Library Resources
Describe your proposal's impact on the University Library's resources, collections, and services. If necessary please consult with the appropriate
disciplinary specialist within the University Library.
Students in the program will rely on the university library for online materials (e.g., books and research papers) and physical books. The program does
not anticipate any special demands on the University Library.
Instructional Resources
Will there be any reduction in other course offerings, programs or concentrations by your department as a result of this new program/proposed
change?
No
Does the program include other courses/subjects impacted by the creation/revision of this program?
No
Financial Resources
How does the unit intend to financially support this proposal?
CS will oversee the proposed Certificate, directed by Teaching Professor Tiffani Williams, and will offer the required classes at least once per year.
Will the unit need to seek campus or other external resources?
No
Are you seeking a change in the tuition rate or differential for this program?
No
Is this program requesting self-supporting status?
No
Market Demand
What market indicators are driving this proposal? If similar programs exist in the state, describe how this program offers a unique opportunity for
students:
The Bureau of Labor Statistics has demonstrated a need for a larger U.S. workforce in computer science. As a result, there has been a rise in coding
bootcamps, MOOC certificates, and micro-credentials in order to gain entry into computing. In October 2020, Eduventures performed a market research
study of our iCAN program. (The proposed Certificate will be offered as part of the iCAN program.) Eduventures analysis details the rise in competition
from coding bootcamps (see attached document, pg 20). Their prediction is that coding bootcamp graduates will outnumber domestic CS master’s
degrees awarded in 2020. While iCAN is not a coding bootcamp, iCAN does appeal to students who may be interested in bootcamps—especially since
a typical student enrolled in a coding bootcamp already possesses a bachelor’s degree. Moreover, Eduventures analysis shows that non-degree/
postbaccalaureate programs are likely to outpace master’s degree growth in the coming years because of speed, convenience, and lower cost (see
attached document, pg 21). The potential to ladder up to a master’s degree is another positive factor for growth of non-degree/postbaccalaureate
certificate programs.

What type of employment outlook should these graduates expect? Explain how the program will meet the needs of regional and state employers,
including any state agencies, industries, research centers, or other educational institutions that expressly encourage the program's development.
Nationwide, there is a strong demand for computing experts in government and public sectors, in corporations of all sizes, in nonprofit organizations,
and in colleges and universities. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, employment in computer
and information technology occupations is projected to grow 11% by 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations. Within computer and
information technology occupations, the employment of software developers is projected to grow 22% by 2029 according to BLS.
What resources will be provided to assist students with job placement?
CS will incorporate recruiting opportunities (such as through its Corporate Connection program) for students in the proposed Certificate program.
Moreover, CS will work to connect students with the Career Center at Illinois as well as Engineering Career Services.
If letters of support are available attach them here:
UIUC_iCAN Program_Final.pdf
Program Regulation and Assessment
Briefly describe the plan to assess and improve student learning, including the program’s learning objectives; when, how, and where these learning
objectives will be assessed; what metrics will be used to signify student’s achievement of the stated learning objectives; and the process to ensure
assessment results are used to improve student learning. (Describe how the program is aligned with or meets licensure, certification, and/or
entitlement requirements, if applicable).
The learning objectives for the program are the following.
• Exhibit proficiency in the design, implementation, and testing of software.
• Demonstrate skills and experience working in small teams in order to solve problems; design, implement, and test code; and learn from one another.
• Apply algorithmic and theoretical computer science principles to solve computing problems from a variety of application areas.
• Demonstrate the ability to learn and develop competencies in specialized or emerging computer science fields.
• Demonstrate the ability to read, analyze, and discuss research papers.
Students will be assigned letter grades appropriate to the course subject.
Every two years we will assess whether students are meeting program goals for each course and survey alumni to measure how effective their training
was for future success. These metrics will then be used to make changes to the program and evaluate if the changes are effective.
There are no licensures or certifications that the program aligns with or needs to meet.
Is the career/profession for graduates of this program regulated by the State of Illinois?
No
Program of Study
“Baccalaureate degree requires at least 120 semester credit hours or 180 quarter credit hours and at least 40 semester credit hours (60 quarter credit
hours) in upper division courses” (source: https://www.ibhe.org/assets/files/PrivateAdminRules2017.pdf). For proposals for new bachelor’s degrees,
if this minimum is not explicitly met by specifically-required 300- and/or 400-level courses, please provide information on how the upper-division hours
requirement will be satisfied.

All proposals must attach the new or revised version of the Academic Catalog program of study entry. Contact your college office if you have
questions.
For new programs, attach Program of Study
GC_Computing Fundamentals_Program of Study.docx
Catalog Page Text
Catalog Page Text: Description of program for the catalog page. This is not official content, it is used to help build the catalog pages for the program.
Can be edited in the catalog by the college or department.
associate dean for graduate, professional and online programs: Harry Dankowicz
overview of admissions & requirements: https://grainger.illinois.edu/academics/graduate
overview of grad college admissions & requirements: https://grad.illinois.edu/admissions/apply
college website: https://grainger.illinois.edu/
address: 402 Engineering Hall, 1308 W Green St, Urbana, Illinois 61801
phone: (217) 244-2745
email: [email protected]
The Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals provides students with Bachelor’s degree or higher in a non-computing discipline with an
accelerated foundation in computing fundamentals. The Graduate Certificate requires four bridging courses in fundamentals of computing and
algorithms and two excursions in computing courses. To allow flexibility and gain deeper knowledge in a computing subject of interest, students are
required to complete an independent study along with a graduate-level elective.
The Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals requires a minimum of 20 credit hours distributed over eight courses as follows. A course
cannot be used to satisfy more than one requirement within the certificate.
Statement for Programs of Study Catalog
Graduation Requirements
Minimum Cumulative GPA:2.75 (as required for awarding of the Campus Graduate Certificate)
Minimum hours required for certificate completion:20 hours
Students who have successfully completed this certificate may use the certificate to satisfy the following degree requirements, subject to department
approval, and provided they apply and are admitted to the degree program:
• 8 hours ofbreadth or elective course coursework for Master of Computer Science
• 8 hours ofbreadth or elective coursework for Master of Science in Computer Science
• 8 hours of required or elective coursework for Master of Science in Bioinformatics: Computer Science
• 8 hours of elective coursework for PhD in Computer Science
* The 8 credit hours of transferrable coursework may not include the bridging courses: CS 400, CS 401, CS 402, and CS 403.
** A letter grade of B or above, or an S is required for transfer.
Coursework Requirements
Code Title Hours
Core Coursework 17
CS400 Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing I (Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing I) 3
CS401 Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms I (Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms I) 3
CS402 Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing II (Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing II) 3

CS403 Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms II (Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms II) 3
CS491 Seminar (Section: Seminar – Excursions in Computing I) 1
CS491 Seminar (Section: Seminar – Excursions in Computing II) 1
CS597 Individual Study 3
Additional Coursework 3
Elective 400-level CS course 3
Total Hours 20
EP Documentation
Attach Rollback/Approval Notices
Re_ Questions Regarding EP 21105_ Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals (UPDATED).pdf
DMI Documentation
Key: 1050

From: Amato, Nancy M
To: Pahre, Jennifer N
Cc: Lehman, Barbara J; Martensen, Kathy; Viswanathan, Mahesh; Williams, Tiffani L
Subject: Re: Questions Regarding EP 21.105: Graduate Certificate in Computing Fundamentals (UPDATED)
Date: Wednesday, April 7, 2021 11:26:44 PM
Attachments: Outlook-gxsladdt.png
Outlook-fgll2nyk.png
(Note: Please consider this version - my previous response was missing the full response to
question 5....)
Hi Jennie,
Thank you again for prompt consideration of our proposal. We are glad to hear you all are as
excited by the program as we are.
I've copied the questions below and followed them with our responses. I'm also copying
Mahesh Viswanathan, our Associate Head for Academics, and Tiffani Williams, our Director
for Onramp Programs. Tiffani has developed the iCAN curriculum and courses, and is one of
the primary instructors in the program. If you have questions, hopefully one of the three of us
can answer them, and if we cannot we'll find someone who can. Please let me know if you'd
like to set up a meeting to talk through any of this.
-Nancy
1. We note that this is a 20-hour program, contemplating two years of completion time.
This seems burdensome for a certificate; it is more in line with a Master’s degree. One
member of my committee worries about the cost, particularly as the proposal notes that
the program will specifically target people from diverse backgrounds. Can you offer
some perspective on why the program requires 20 hours?
Response: The iCAN curriculum is designed for completion in one year, 3 semesters
(fall, spring, summer). In the proposal, we were required to enter the longest length of
time (2 years) to complete the program and not the average length of time (1 year). The
longest length of time is based on the maximum time requirement for a Campus
Graduate Certificate.
The minimum number of credit hours required for a Campus Graduate Certificate is 12
hours. The iCAN program is 8 hours over the minimum requirement. We believe these
additional hours over the minimum requirement offers a credential that provides depth
and breadth in computing fundamentals from a top 5 computer science department.
Moreover, the additional 8 hours can be applied towards a graduate degree in computer
science.
The iCAN curriculum is modeled after Northeastern’s 16-hour Align program
(https://bit.ly/2OuxfPn). The Align bridging program does not lead to a credential. As
a result, Align students have the foundation to enter Northeastern’s 32 credit hour
MSCS degree program. (4 hours of the Align program transfer to the MSCS.) In
general, students with little or no background in computing do not have the CS
background to be admitted to CS graduate programs. Bridging programs like iCAN

and Northeastern Align provide a pathway to a Masters or PhD degree in computer
science.
In terms of cost, since the iCAN program will offer a Campus Graduate Certificate, it
is expected that iCAN students will have access to federal financial aid. The iCAN
program is working with corporate and philanthropic partners to offer scholarships. For
example, the iCAN program has received a $325K donation from FaceBook.
2. Only 8 hours of credits will transfer if students wish to pursue a master's degree. What
is the reason for this?
Response: There are 12 hours of CS bridging courses (CS 400, CS 401, CS 402, CS
403), which cannot be used for graduate credit in CS. The remaining 8 hours of the
iCAN program can be used for graduate credit. Thus, 8 out of 20 (or 40%) credits are
transferable for graduate credit in CS.
In comparison, 4 out of 16 hours (or 25%) of Northeastern Align’s bridging credits are
transferable for graduate credit in CS.
3. This certificate is already listed on the iCAN website and applications for fall 2021 are
open. Yet, this proposal is not yet approved. This sometimes happens when staff in
units get ahead of the process. Is that what happened here?
Response: Currently, the iCAN program offers a “little c” certificate, which is
approved at the department level. There are relatively few restrictions or requirements
on “little c” certificates. As such, “little c” certificates are not transcriptable nor
eligible for federal financial aid.
Our proposal is for a “big C” certificate or Campus Graduate Certificate, which comes
with a number of benefits that include being transcriptable as well as access to federal
financial aid.
Our pilot cohort, which started in Fall 2020, is for a “little c” certificate. We expect to
have our first graduating class in Summer 2021.
4. Large enrollment is expected downstream (200 by the fifth year). How will the
administrative burden be managed—is there approval to hire a coordinator?
Response: We are currently interviewing for a iCAN Program Specialist/Coordinator
and Academic Specialist (Job ID: 138975). We expect to have this person on board in
May 2021.
5. Multiple required courses (CS 400-403) are listed as not existing yet, but it looks in
CIM like they were all recently approved. (It seems to me that this is a simple timing
issue.) The proposal says that no additional resources are needed because these courses
are already being taught (but it is not clear if that is true for CS 400-403). If these are

new courses, are instructors lined up to teach them.
Response: The material for the CS 400-403 courses has been first taught in CS
498 courses in Fall 2020 and Spring 2021 by Profs. Yael Gertner and Tiffani
Williams. Starting in Fall 2021, both professors will be able to offer their
previously taught CS 498 courses as regularly scheduled CS 400-403 courses.
Thus, we do not see any additional resources required for teaching these courses.
On 4/7/21 12:58 PM, Pahre, Jennifer N wrote:
Nancy,
Thank you for your very prompt reply. I look forward to your response, and we
can certainly chat on Friday if further clarification would be helpful.
All best,
Jennie
_____________________________________________
Jennifer N. Pahre
Director of Undergraduate Studies
Assistant Teaching Professor
University of Illinois College of Law
504 East Pennsylvania Avenue
Champaign, Illinois 61820
Pronouns: She/her/hers
Under the Illinois Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), any written communication to or
from University employees regarding University business is a public record and may be
subject to public disclosure.
From: Amato, Nancy M <[email protected]>
Sent: Wednesday, April 7, 2021 12:55 PM
To: Pahre, Jennifer N <[email protected]>
Cc: Lehman, Barbara J <[email protected]>; Martensen, Kathy
Subject: Re: Questions Regarding EP 21.105: Graduate Certificate in Computing
Fundamentals
Hi Jennie,
Thanks for your interest/support - we are excited about iCAN as well. We'll read
your questions carefully and prepare a response - I'll try to get back to you by

tomorrow. It might be helpful for us to also discuss them in case there are any
questions based on our written response and I'd be happy to set up a time to talk
tomorrow or Friday if you would find that useful. Please let me know.
-Nancy
On 4/7/21 12:47 PM, Pahre, Jennifer N wrote:
Dear Professor Amato,
I hope your week is going well.
I’m currently the head of Subcommittee A of the Senate Educational
Policy Committee. Our subcommittee was assigned the task of
reviewing EP.21.105, the proposal is to create a new graduate
certificate in Computing Fundamentals.
The subcommittee is firmly in favor of the proposal. We think that
broadening CS training so that non-CS majors can be ready to enter
CS fields is an excellent undertaking.
Several members of my subcommittee had a few questions, and as
you are the listed sponsor, I'm reaching out for your thoughts. If
possible, I would like to address these questions before the next
meeting (on Monday), to facilitate the proposal’s swift approval.
1. We note that this is a 20-hour program, contemplating two
years of completion time. This seems burdensome for a
certificate; it is more in line with a Master’s degree. One
member of my committee worries about the cost, particularly
as the proposal notes that the program will specifically target
people from diverse backgrounds. Can you offer some
perspective on why the program requires 20 hours?
2. Only 8 hours of credits will transfer if students wish to pursue a
master's degree. What is the reason for this?
3. This certificate is already listed on the iCAN website and
applications for fall 2021 are open. Yet, this proposal is not yet

approved. This sometimes happens when staff in units get
ahead of the process. Is that what happened here?
4. Large enrollment is expected downstream (200 by the fifth
year). How will the administrative burden be managed—is
there approval to hire a coordinator?
5. Multiple required courses (CS 400-403) are listed as not
existing yet, but it looks in CIM like they were all recently
approved. (It seems to me that this is a simple timing issue.)
The proposal says that no additional resources are needed
because these courses are already being taught (but it is not
clear if that is true for CS 400-403). If these are new courses,
are instructors lined up to teach them.
I look forward to your response and thank you in advance for your
kind assistance.
Best regards,
Jennie Pahre
_____________________________________________
Jennifer N. Pahre
Director of Undergraduate Studies
Assistant Teaching Professor
University of Illinois College of Law
504 East Pennsylvania Avenue
Champaign, Illinois 61820
Pronouns: She/her/hers
Under the Illinois Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), any written
communication to or from University employees regarding University business
is a public record and may be subject to public disclosure.
--
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Nancy M. Amato
Abel Bliss Professor and Head, Department of Computer Science

University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
2232 Siebel Center, 201 N. Goodwin Ave., Urbana IL 61801
+1-217-333-3426, [email protected]
[email protected] (for scheduling or administrative contact)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
PS. I have multiple openings for postdocs - pls share with your
students
and others: http://cobotfactory.web.illinois.edu/
PPS. Check out iCAN (Illinois Computing Accelerator for Non-
Specialists),
a 1-year program for non-computing college graduates. A bridge to a
career
in tech or grad studies. Applications for our second cohort are
open now!
http://cs.illinois.edu/ican
--
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Nancy M. Amato
Abel Bliss Professor and Head, Department of Computer Science
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
2232 Siebel Center, 201 N. Goodwin Ave., Urbana IL 61801
+1-217-333-3426, [email protected]
[email protected] (for scheduling or administrative contact)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
PS. I have multiple openings for postdocs - pls share with your students
and others: http://cobotfactory.web.illinois.edu/
PPS. Check out iCAN (Illinois Computing Accelerator for Non-Specialists),
a 1-year program for non-computing college graduates. A bridge to a career
in tech or grad studies. Applications for our second cohort are open now!
http://cs.illinois.edu/ican

PROGRAM OF STUDY
Requirements
Core Coursework
17
CS 400 Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing I 3
CS 401
Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms I
3
CS 402
Accelerated Fundamentals of Computing II
3
CS 403
Accelerated Fundamentals of Algorithms II
3
CS 491
Seminar – Excursions in Computing I
1
CS 491
Seminar – Excursions in Computing II
1
CS 597 Individual Study 3
Additional Coursework
3
Elective 400-level CS course
Total Hours
20
Other Requirements and Conditions (may overlap)
Minimum Cumulative GPA: 2.75 (as required for awarding of the Campus Graduate Certificate)
.
.

University of Illinois – Urbana Champaign
October 2020
Illinois Computer Accelerator
for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-
Degree Program

2
Table of Contents
About the Study
Project Background
Methodology
Key Findings
Research Findings
Program Demand
Competitive Landscape
Competitive Insights
Labor Market Demand
Prospective Adult Students

About the Study
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

4
Project Background
University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign (UIUC)
Urbana-Champaign, IL
PROGRAM: Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program
UIUC recently launched the iCAN (Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists) non-degree program, which will enroll its first set of students in
the 2020-2021 academic year. The program is a three semester (fall, spring, summer), full-time non-degree program. Students will receive a
“computer fundamentals certificate” upon completion, as well as a number of graduate-level computer science credits. The program will be offered
on UIUC’s Urbana-Champaign campus, but eventually in Chicago as well as via an online format. Although the program was designed to be face-
to-face, it will be offered via distance learning in the upcoming academic year because of COVID-19. Targeted to students with a bachelor’s degree,
the program is designed for students without a computer science-related background who are interested in learning more about the field or making
a career switch. The program also focuses on broadening participation in computer science and aims to focus on populations that are
underrepresented in computer science (i.e., women, Black/African American and Latinx groups). The first two semesters of iCAN act as an on-
ramp. The third semester acts as an off-ramp, which includes a group research project with a faculty member or a project related to industry
depending on the students’ intended outcomes. The third semester will be offered either as a group research project with a faculty member or a
project related to industry depending on the students’ intended outcomes. Program outcomes are envisioned as two pathways: 1) graduate degree
(Masters or PhD ) in computer science; or 2) entry-level tech role.
The key research questions addressed in this study are:
• What is the overall health of the computer science market given supply and demand
indicators?
• What are some key characteristics of potential competitors for UIUC, and how can UIUC
differentiate its proposed program?
• Are there any other similar programs with the goal of directly appealing to or increasing
engagement of the underrepresented populations in the computer science industry?

5
Methodology
Program Demand
Eduventures consulted the National Center for Education Statistics’ (NCES) Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) database to analyze national degree conferral and
provider trends for the years 2014-2019, as reported to the Classification of Instruction Program Codes (CIP Codes). Analyzed CIP codes for this study can be found on slide 6. The region for
this study is defined as the following states: Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Ohio, and Wisconsin. Eduventures also provided insights from previous research
to gain further insights into the market.
Competitive Landscape
Eduventures consulted IPEDS degree completions data for the selected CIP codes to identify institutions nationally and regionally reporting relevant post baccalaureate certificates and
provided their 2019 conferrals, compound average growth rate (CAGR), year-over-year growth rate, program name, whether their program targets those without a computer science
background, and whether the program seeks to increase access in the field. The study focuses on postbaccalaureate certificates as these are the credential that most closely aligns to the
iCAN program. Eduventures also conducted a targeted web scan to identify additional providers and included examples of relevant courses or programs from MOOC platforms, as well as
master’s degree programs in line with iCAN.
Competitive Insights
Leveraging a web scan and program demand data from IPEDS, Eduventures identified aligned or relevant programs to provide competitive analysis. Information collected in this review
includes information on modality, program structure, whether graduate credits are earned, admissions information, curriculum notes, pricing, target audience, marketing themes, career
outcomes and curriculum details.
Labor Market Demand
Eduventures analyzed projected growth for SOC codes aligned to the iCAN program in order to provide additional insights into the viability of the proposed program. Relevant SOC codes can
be found on slides 7-8.
Prospective Adult Survey
Eduventures analyzed proprietary data from the Eduventures June 2020 Adult Prospect Survey to learn more about adult prospective students interested in certificate programs
(undergraduate and graduate). Eduventures relied on national data (n=2,270) as well as data on adults who said they were interested in returning to school for a certificate program (n=124).
Eduventures leveraged the following data sources to investigate the market for this program:
Program
Demand
Competitive
Landscape
Competitive
Insights
Labor Market
Demand
Prospective
Adult Survey

6
Methodology
CIP Codes Program Description
Computer and Information
Sciences (11.0101)
A general program that focuses on computing, computer science, and information science and systems. Such programs
are undifferentiated as to title and content and are not to be confused with specific programs in computer science,
information science, or related support services.
Computer Science (11.0701) A program that focuses on computer theory, computing problems and solutions, and the design of computer systems and
user interfaces from a scientific perspective. Includes instruction in the principles of computational science, computer
development and programming, and applications to a variety of end-use situations.
Source: NCES.
Eduventures examined the following CIP Codes related to the iCAN program to assess degree conferral and
provider trends:
The CIP codes selected above were chosen as Eduventures analysis shows that institutions tend to use both CIP codes
for computer science-aligned programs. It is important to note that Eduventures research has found that programs
related to computer science, cybersecurity, and information technology are all reported to these CIP codes.

7
Methodology
Source: BLS.
CIP Codes Program Description
Computer and Information
Research Scientists (15-111)
Conduct research into fundamental computer and information science as theorists, designers, or inventors. Develop solutions to problems in the
field of computer hardware and software.
Computer and Information
Systems Managers (11-3031)
Plan, direct, or coordinate activities in such fields as electronic data processing, information systems, systems analysis, and computer
programming. Excludes "Computer Occupations" (15-1211 through 15-1299).
Computer Network Architects
(15-1241)
Design and implement computer and information networks, such as local area networks (LAN), wide area networks (WAN), intranets, extranets,
and other data communications networks. Perform network modeling, analysis, and planning, including analysis of capacity needs for network
infrastructures. May also design network and computer security measures. May research and recommend network and data communications
hardware and software. Excludes "Information Security Analysts" (15-1212), "Computer Network Support Specialists" (15-1231), and "Network and
Computer Systems Administrators" (15-1244).
Computer Network Support
Specialists (15-1152)
Analyze, test, troubleshoot, and evaluate existing network systems, such as local area networks (LAN), wide area networks (WAN), cloud
networks, servers, and other data communications networks. Perform network maintenance to ensure networks operate correctly with minimal
interruption. Excludes "Computer Network Architects" (15-1241) and "Network and Computer Systems Administrators" (15-1244).
Computer Programmers
(15-1131)
Create, modify, and test the code and scripts that allow computer applications to run. Work from specifications drawn up by software and web
developers or other individuals. May develop and write computer programs to store, locate, and retrieve specific documents, data, and information.
Computer Systems Analysts (15-
1211)
Analyze science, engineering, business, and other data processing problems to develop and implement solutions to complex applications
problems, system administration issues, or network concerns. Perform systems management and integration functions, improve existing computer
systems, and review computer system capabilities, workflow, and schedule limitations. May analyze or recommend commercially available
software.
Eduventures examined the following SOC Codes aligned to the iCAN program:

8
Methodology
Source: BLS.
CIP Codes Program Description
Database Administrators
(15-1242)
Administer, test, and implement computer databases, applying knowledge of database management systems. Coordinate changes to computer
databases. Identify, investigate, and resolve database performance issues, database capacity, and database scalability. May plan, coordinate, and
implement security measures to safeguard computer databases. Excludes "Information Security Analysts" (15-1212) and "Database Architects"
(15-1243).
Information Security Analysts (15-
1122)
Plan, implement, upgrade, or monitor security measures for the protection of computer networks and information. Assess system vulnerabilities for
security risks and propose and implement risk mitigation strategies. May ensure appropriate security controls are in place that will safeguard digital
files and vital electronic infrastructure. May respond to computer security breaches and viruses. Excludes "Computer Network Architects" (15-
1241).
Network and Computer Systems
Administrators (15-1142)
Install, configure, and maintain an organization's local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), data communications network, operating
systems, and physical and virtual servers. Perform system monitoring and verify the integrity and availability of hardware, network, and server
resources and systems. Review system and application logs and verify completion of scheduled jobs, including system backups. Analyze network
and server resource consumption and control user access. Install and upgrade software and maintain software licenses. May assist in network
modeling, analysis, planning, and coordination between network and data communications hardware and software. Excludes "Information Security
Analysts" (15-1212), "Computer Network Support Specialists" (15-1231), and "Computer User Support Specialists" (15-1232).
Software Developers (15-1132) Research, design, and develop computer and network software or specialized utility programs. Analyze user needs and develop software solutions,
applying principles and techniques of computer science, engineering, and mathematical analysis. Update software or enhance existing software
capabilities. May work with computer hardware engineers to integrate hardware and software systems, and develop specifications and
performance requirements. May maintain databases within an application area, working individually or coordinating database development as part
of a team.
Web Developers (15-1134) Develop and implement websites, web applications, application databases, and interactive web interfaces. Evaluate code to ensure that it is
properly structured, meets industry standards, and is compatible with browsers and devices. Optimize website performance, scalability, and server-
side code and processes. May develop website infrastructure and integrate websites with other computer applications. Excludes "Special Effects
Artists and Animators" (27-1014).
Eduventures examined the following SOC Codes aligned to the iCAN program:

Executive Summary
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

10
Key Findings
− Program demand shows overall growth in computer science market with small number of certificates, though non-degree market shows strong potential. Overall, the
computer science market has shown growth in the last few years with bachelor's and master's degrees dominating the market. Though the certificate market is small, declines in
master's degrees in the field and multiple indicators for future non-degree market growth point to strong potential. The recent growth of non-degree programs (particularly
bootcamps) as well as Eduventures projections for growth of non-degree programs are especially key for iCAN.
− An overview of the competitive landscape shows few providers that specifically target those without a computer science background and none that focus on
increasing access to underrepresented populations. NCES IPEDS data and a targeted web scan show few higher education providers with relevant non-degree programs,
and MOOC platforms offer few relevant programs or courses. Eduventures analysis does reveal a handful of master's degree programs that are in line with iCAN’s proposed
format, as well as a new school (College of Computing) being launched by MIT that may act as a competitor in the future.
− Competitive analysis shows marketing focus on programs' target audience and entry to master's program, but career outcomes are not detailed. Almost all the
examined programs are offered on-campus with only one having an online modality. UIUC's pricing for in-state students is on the low end of the examined competitors but the out-
of-state cost is on the high end. Marketing themes generally focus on the idea of career advancement, as well as entry to a master's program, but detailed information on career
outcomes is not typical. Curriculum offerings have little flexibility for students in coursework selection with several programs offering choice in one or two elective courses.
− Labor market points to bachelor's degree as point of entry for aligned occupations and projects almost all occupations to have above average growth with computer
programmers as exception. Both nationally and regionally*, computer programmers are projected to have negative growth with the regional market showing a faster decline in
growth for the occupation. Information security analysts and software developers are two occupations that show especially strong growth, though growth for software developers
is a bit slower at the regional level.
− Adult learners show increased preference for online study in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as focus on career advancement and affordable, customizable
programs. Analysis of adult prospects’ modality preferences shows an increase in preference for online during COVID-19 and a sustained interest when prospects are asked
about their preferences in the future (when COVID is believed to no longer be a factor). Earning more money is important for certificate prospects, as well as getting a better job in
their field or switching careers. Affordable tuition and fees, as well as interactions with faculty, are other important factors for adult prospects interested in certificate programs.
*UIUC’s broader region is defined as the following states: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Ohio, Wisconsin

11
Recommendations
Although iCAN appears to be a unique offering in the current market, trends in both the computer science and non-degree markets show strong potential for the program,
especially paired with solid labor market projections and the strong connection to career outcomes within the program. As iCAN considers next steps for the program,
Eduventures offers the following recommendations:
− Monitor trends in master’s and non-degree markets in computer science. Eduventures analysis shows that there has been a recent decrease in master’s degrees
in computer science programs, as well as projected growth for the general non-degree market. Although this decrease is related to a number of factors, including a
decrease in international students, it is also likely driven by students interest in shorter, less costly options, which is evidenced by interest in computer science
bootcamp programs.
− Emphasize focus on increasing access as key program differentiator. None of the programs that Eduventures reviewed in this study note that they focus on
increasing access in the computer science field for underrepresented groups. This is a unique component of the iCAN program and one that stakeholders should use
as a key differentiator for iCAN. Currently, the program website notes this aspect of iCAN, but it should be further detailed in marketing and recruitment materials.
− Continue to highlight benefits of studying at UIUC, especially to demonstrate value of program. The iCAN website clearly states the program’s target audience,
as well as highlights the benefits of studying at UIUC, such as faculty involvement and academic and career advising. These program features are especially important
because they clearly differentiate iCAN from other competitors such as bootcamps or MOOC offerings, which offer a less costly option for students
− Specific career outcomes of iCAN are key and set the program apart from master’s bridge programs. Other programs in line with iCAN tend to focus on a
pathway to a master’s degree as the key outcome of the program, noting credits can be transferred into the credential. The fact that iCAN focuses on this pathway is
key and will help to differentiate the program, especially for certificate prospects that are focused on career advancement. Clearly listing these outcomes on the
program website, such as by including relevant job titles and income potential, is one way to emphasize this aspect of the program.
− Planned online modality will help to draw additional students. The iCAN stakeholders plan to offer the program at an additional location, as well as via an online
modality in the future. Based on the preferences of adult prospects, this option will help to draw additional students, especially as the preference this modality may
continue to have even beyond the impact of COVID-19.

Program Demand
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

13
Program Demand. An introduction to the overall computer science and
certificate markets.
First, in order to provide insights on the larger computer science market, Eduventures provides data from IPEDS- the
primary source for degree conferral and certificate completion data from U.S. colleges and universities.
The following slides provide data and analysis for the aligned CIP codes* in this study for the following market levels:
• All conferrals and completions for degree and non-degree credentials (at both the national and regional levels) to
provide a high-level look at the computer science market
• Breakdown of all 2019 conferrals/completions by program type (at both the national and regional levels) to
provide a high-level look at the computer science market
• Post-baccalaureate completions (at both the national and regional levels) to provide insights on the most closely
aligned credential to the iCAN non-degree program. It is important to note that non-degree completions data is
not comprehensive due to reporting issues in NCES IPEDS, see slide 19 for more information on this
• Master’s conferrals (at both the national and regional levels) since one of iCAN’s stated program outcomes is a
computer science master’s degree
*See slide 6 for more information on CIP codes used in this study. As stated on slide 10, conferrals/completions for these CIP codes likely include computer science, cybersecurity,
and information technology programs.

14
Program Demand: All Computer Science aligned conferrals/completions
show strong growth in larger market.
51,830
60,913
73,503
84,344
90,409
93,914
11,090
12,918
16,501
19,494
19,187
19,127
0
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
80,000
90,000
100,000
2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
All Conferrals/Completions
National Regional
• 2014-2019 National Conferral/Completions
CAGR*: 13%
• 2014-2019 Regional Conferral/Completions
CAGR*: 12%
• Overall, both the national and regional markets
for computer science saw conferral/completions
growth when looking at all degree levels.
• The national market shows consistent growth
with especially strong growth between 2014 and
2017. The regional market also saw strong
growth during this time period though there was
a flattening between 2017 and 2019 with a slight
decrease in conferrals between 2018 and 2019.
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi
All for-credit program conferrals or completions reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
*Compound Annual Growth Rate
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
In order to examine the larger market for Computer Science, Eduventures looked at conferrals/completions for all
degrees reported to the two aligned CIP codes at the national and regional levels.

15
Program Demand: All computer science conferrals/completions show that
bachelor’s and master’s degrees dominate market.
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi
All for-credit program conferrals or completions reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
*Percentages add up to greater than 100% due to rounding
^Undergraduate certificates defined as “Award of less than 1 academic year” and “Award of at least 1 but less than 2 academic years” in IPEDS
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
8%
9%
58%
1%
23%
1%
17%
4%
55%
1%
21%
2%
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
UG Certificate Associate Degree Bachelor's Degree Postbacc Certificate Master's Degree Doctorate Degree
2019 Computer Science Conferrals/Completions by Degree Type*
National
Regional
Bachelor’s and master’s
degrees dominate the market
with roughly 80% of the market
share at both the national and
regional levels.
Postbaccalaureate
certificates make up
a tiny portion of the
computer science
market both
nationally and
regionally.
Next, Eduventures reviewed conferrals/completions for all degree levels for the aligned CIP code in 2019.

16
Program Demand: Postbaccalaureate certificate market is small but
growing, especially at regional level.
179
208
204
156
286
277
34
57
78
42
107
106
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Computer Science Postbaccalaureate Certificate Completions
National Regional
• 2014-2019 National Completion CAGR*: 9%
• 2014-2019 Regional Completion CAGR*: 26%
• Eduventures analyzed completions for the
postbaccalaureate certificate market as this
credential aligns most closely to the iCAN
program. It is important to note that NCES
IPEDS does not capture the entire certificate
market (please see slide 19 for more details).
• Completions for aligned postbaccalaureate
certificates also show overall growth for both the
national and regional markets, though the
number of completions is small for both with
some volatility in reported completions.
• Regional completion CAGR far outpaced
national CAGR significantly, though again the
number of completions was small.
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi
Postbaccalaureate certificate completions reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
*Compound Annual Growth Rate
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
Eduventures also analyzed completions for postbaccalaureate certificates at the national and regional levels as these
most closely align the iCAN program.
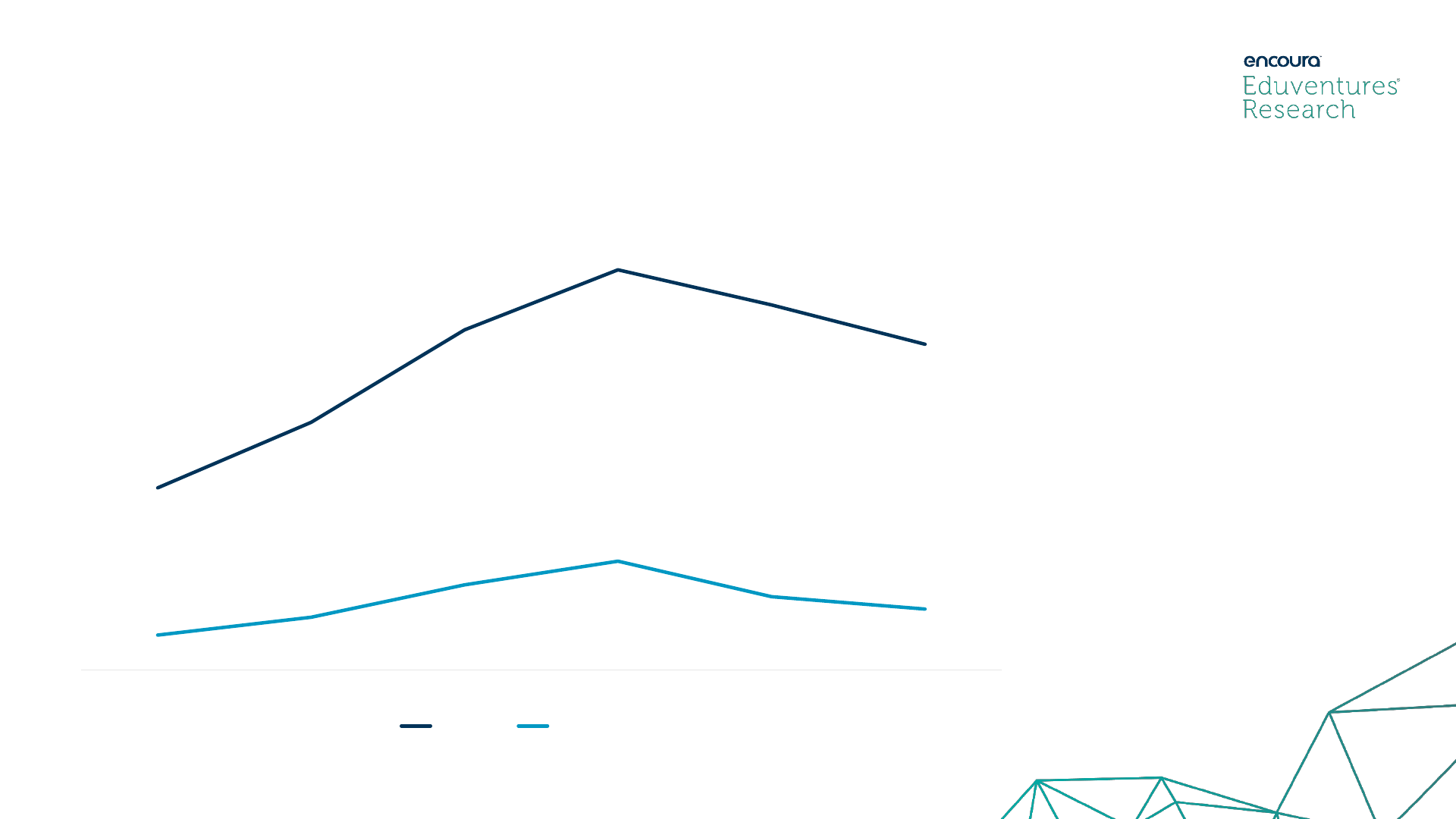
17
Program Demand: Master’s market shows rapid growth then conferral
declines in recent years.
11,947
16,241
22,289
26,223
23,931
21,346
2,301
3,471
5,586
7,139
4,813
3,999
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
30,000
2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Computer Science Master’s Completions
National Regional
• 2014-2019 National Completion CAGR*: 12%
• 2014-2019 Regional Completion CAGR*: 12%
• Eduventures also reviewed the computer
science master’s market since iCAN
stakeholders indicated this as a potential
program outcome for students.
• Overall, there has been growth in master’s
conferrals in computer science for both the
national and master’s market, though recent
trends show a decline in conferrals.
• For both the national and regional markets,
there was very strong growth between 2014 and
2017 followed by declines in 2018 and 2019.
This could signal that the computer science
master’s market has tapped out and is now in
decline.
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi
Master’s degree conferrals reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
*Compound Annual Growth Rate
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
Eduventures also analyzed completions for master’s degree at the national and regional levels as this is a program
outcome of interest for the iCAN program.

18
Program Demand. Further insights on computer science non-degree
market.
Since the non-degree market is difficult to track and requires other approaches to gauge market size, the next three slides
focus on research that Eduventures has conducted related to both measuring the certificate market, as well as insights on
the market for computer science certificates specifically.
The following three slides include insights from various Eduventures publications related to program demand for iCAN:
• Wake Up Call on how NCES IPEDS data does not capture the entire certificate market
• Wake Up Call on recent computer science market trends with a focus on the certificate market and the role of
bootcamps
• Report on graduate enrollment projections and the role of the non-degree credential

19
Program Demand: IPEDS reporting on certificate data is incomplete.
Source: Eduventures Wake Up Call: https://encoura.org/are-certificates-really-booming-an-unsolved-mystery/
Eduventures analysis, including this Wake Up Call from 2018, has long shown that certificate reporting to NCES IPEDS
does not capture all completions, which could explain the low number of Computer Science certificates reported.
Eduventures analysis of IPEDS data shows
growth for undergraduate certificates over the last
twenty years, although bachelor’s degrees saw
stronger growth and still dominates the market in
terms of size.
Although institutions are required to report certificate
completions, it is easy to find examples of
institutions not doing so. MOOC and micro-
credentials further confuse the market. It is important
to keep this in mind when reviewing certificate
completions to IPEDS as additional programs are
likely not being reported.

20
Program Demand: Eduventures analysis details the rise in competition
from coding bootcamps in the computer science market.
• A Wake Up Call article published by Eduventures’ Chief Research
Officer in January 2020 titled Higher Education Predictions for 2020:
Recession Certificates, and Computer Science includes analysis on
recent computer science master’s trends.
• One prediction states that coding bootcamp graduates will outnumber
domestic master’s degrees awarded for the first time in 2020.
• Though domestic master’s degree awards have continued to rise, their
growth does not match that seen by the total market that was mostly
driven by international demand from 2014-2017, which leveled off in
2018.
• Both the decline in computer science master’s conferrals and the
potential for bootcamps are important for iCAN stakeholders to consider.
It will be important for UIUC to consider both differentiation and
adaption.
• Differentiation: what can iCAN offer that a bootcamp cannot?
(e.g. access to career services, more in-depth coursework)
• Adaption: what popular features from a bootcamp can a
master’s program adopt? (e.g. shorter off-ramps, affordability)

21
Program Demand: Non-degree program growth likely to outpace
master’s degree growth in coming years.
• Eduventures recently published a report on graduate
enrollment projections titled Fall 2020 Enrollment Scenarios:
Part 4, Graduate Enrollment, which looked at growth for the
domestic master’s market and the potential impact of the non-
degree market.
• Although the master’s degree market has always competed
with non-degree credentials that are shorter and lower cost,
the competition in this space has grown significantly with
several new providers entering the market in recent years.
• Although both the master’s and non-degree markets will
receive a boost in enrollment as a result of COVID-19,
Eduventures predicts that economic retraction and uncertainty
will increase the appeal of non-degree alternatives, which
offer speed, convenience, and low price. Indeed, we predict
that the master’s market will ultimately begin to shrink.
• It is important to note that these markets need not be
exclusive, especially with the potential to ladder up to a
master’s degree from a non-degree credential.

Competitive Landscape
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

23
Competitive Landscape. A closer look at potential competitors.
The next section of this report takes a closer look, quantitatively and qualitatively, at potential competitors for the iCAN program.
Eduventures leveraged both NCES IPEDS data and programmatic websites to conduct this analysis.
Eduventures focused on the competitive landscape in four layers:
1. Top providers for computer science postbaccalaureate certificates (the credential that most closely aligns with the ICAN
program), nationally and regionally, as reported to NCES IPEDS. Eduventures provided details on 2019 completions, 2018-
19 year-over-year growth, and 2014-19 CAGR, as well as whether the program targets prospects with a non-computer
science background and whether the program focuses on increasing access to underrepresented populations. Eduventures
did not include any information technology, cybersecurity, or similar certificate programs.
2. Providers found via a targeted web scan for similar programs and via a web scan of the top twenty providers of computer
science master’s programs (identified via NCES IPEDS), as well as whether the program targets prospects with a non-
computer science background and whether the program focuses on increasing access to underrepresented populations.
3. Other potential competitors that offer computer science master’s programs that target those with no computer science or
programming background.
4. MOOC platform (Coursera, edX) courses or programs worth consideration as competitors for the UIUC iCAN program.

24
Competitive Landscape: National postbaccalaureate certificates show mostly
small completion rates with no stated focus on increasing access.
Provider
Certificate
Completions
(2019)
Growth %
YOY
(
2018-
19)
Completion
CAGR
2014-19
Program Name (Website Link)
Does
program target those
without CS background?
Focus on increasing access
for underrepresented
populations in CS?
University of
Wisconsin
-
Madison
70 13%
N/A**
Certificate in Computer Sciences
Yes
- Only for Wisconsin
undergraduates enrolled in non
-
computer science certificate
Not listed
Seattle University
37 3%
N/A**
Computer Science Fundamentals
Graduate Certificate
Yes
-
No programming knowledge
or experience required, any
bachelor’s degree accepted
Not
listed
Kennesaw
State
University
28 155%
N/A**
Graduate Certificate in Computer
Science Foundations
No
- Program targets computer
science students or working
professionals in field
Not
listed
Drexel University*
13 30%
N/A**
Online Certificate in Computer
Science***
Yes
- Program suitable for those
with a bachelor’s in a non
-
computer science field
Not
listed
Virginia
Commonwealth
University
9 50%
-39%
Baccalaureate Certificate in the
Fundamentals of Computing
Yes
- Only for those with non-
technical backgrounds, VCU
undergraduates can enroll
Not
listed
University of Texas
at San Antonio
7 250%
N/A** Coding Bootcamp***
Yes
- Technical background not
required
Not listed
New Jersey
Institute of
Technology
6 -25%
-250% Certificate in Computer Science
Unclear
-
Notes skills gained are
relevant for computer science
professionals
Not listed
Missouri
University of
Science &
Technology
*
6 -50%
15%
Graduate Certificate in
Computational Intelligence
No
- Program
is for students with
engineering background
Not listed
University
of
Massachusetts
-
Dartmouth*
3 50%
N/A**
Computer Science Graduate
Certificate
Somewhat
- Students with non-
computer science background
have required pre
-req
coursework
Not listed
Tufts
University 2 100%
N/A**
Post
-Baccalaureate
or Certificate
in Computer Science
Depends
on program-
Postbacc
program requires one comp
science course, certificate for com
science professionals
Not listed
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi.
Post baccalaureate certificate completions as reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
Only computer science programs were included in this analysis, information technology and cybersecurity programs were excluded.
Bold orange font=Located in UIUC’s region; Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
*Program offered via online modality
**Did not report completions in 2014
^^Also offers Distributed Computing graduate badge; ***It is unclear if completions the UTSA is reporting align to this program or not as UTSA offers several potentially relevant certificates, but this program most closely related to computer science
• Eduventures reviewed the top ten
postbaccalaureate certificate programs as
reported to IPEDS in 2019 that offer
relevant programs. Overall, completions
were low with the exception of the top few
providers, though many programs show
short-term growth. Most programs also
appear to be newer and began reporting
conferrals in the last couple of years.
• There were mixed findings for programs
that target those without a computer
science background with four of the top ten
specifically targeting this population. No
program includes language that shows their
goal is to increase access to computer
science for underrepresented populations.
• Though the Wisconsin program has the
highest number of conferrals, it is only
available for enrolled undergraduate
students and is more akin to a minor versus
a separate degree program.

25
Competitive Landscape: Few regional postbaccalaureate certificates found
and only Wisconsin has significant number of completions.
Provider
Certificate
Completions
(2019)
Growth %
YOY
(
2018-
19)
Completion
CAGR
2014-19
Program Name
(Website Link)
Does program target those
without CS background?
Focus on increasing access for
underrepresented
populations in
CS?
University of
Wisconsin
-
Madison
70 13%
N/A**
Certificate in
Computer Sciences
Yes
- Only for Wisconsin
undergraduates enrolled in non
-
computer science certificate
Not listed
Missouri University
of Science and
Technology*
6 -50%
15%
Graduate Certificate in
Computational
Intelligence
No
- Program is for students with
engineering background
Not listed
Grand Valley State
University
1 -100%
-37%
Software Engineering
Graduate Badge^
No
- Program
requires evidence of
programming skills
Not listed
Source: NCES IPEDS through Emsi.
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
Note: Only computer science programs were included in this analysis, information technology and cybersecurity programs were excluded
Post baccalaureate certificate completions as reported to the two aligned CIP Codes: Computer and Information Sciences (11.0101); Computer Science (11.0701)
*Program offered via online modality
**Did not report completions in 2014
^^Also offers Distributed Computing graduate badge
• Only three providers were found in UIUC’s
region that reported completions for a
computer science postbaccalaureate
certificate. Of these providers, Wisconsin had
the highest number of completions with 70 in
2019.
• Only Wisconsin targeted prospects with a
non-computer science background, though
their program appears to only be for
Wisconsin undergraduate students enrolled
in a non-computer science bachelor’s
degree. The other two providers offer
certificates for those with computer science
or programming backgrounds.
• In line with the national market, none of the
examined providers include any language on
their websites on increasing access for
underrepresented populations.

26
Other Competitors: Web scan reveals few additional relevant programs again
with no focus on increasing access.
Provider
Program Name (Website
Link)
Does program target those without CS background?
Focus on increasing access for
underrepresented populations?
Boston University
Certificate in Computer
Science
Unclear- Target audience not listed but coursework may be
advanced
Not listed
Columbia University
CS@CU MS Bridge Program
in Computer Science
Yes-
Program targets those without any background in field, can
be a bridge to master’s program
Not listed
Harvard Extension School
Programming Certificate
Yes- Program designed for those with little or no computer
programming experience
Not listed
Loyola University Chicago*
Computer Science Certificate
Somewhat- Program notes no experience required but that
coursework is “rigorous”
Not listed
New York University
PAC Program of Introductory
Courses
Yes- Targets those without any background in field who wish to
enter a master’s program
Not listed
North Carolina State
University*
Computer Programming
Certificate
Yes- Targets those who wish to change careers or learn more
about the field
Not listed
Northeastern University
Computer Science, Graduate
Certificate
Yes- Program targets those who wish to advance skills or move
on to master’s degree (program complete prereqs for
Northeastern’s master’s degree
Not listed
Stanford University Online*
Foundations of Computer
Science Graduate Certificate
Somewhat- Bachelor’s degree in any field but some
programming background required
Not listed
University of Miami
Post Baccalaureate Certificate
in Computer Science
Yes- Designed for those with a bachelor’s in a non-computer
science field
Not listed
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
*Program offered via online modality
• Eduventures also conducted a web scan
to find relevant programs in computer
science not reported to IPEDS, including
a scan of the top 20 national providers of
master’s degrees in the field. An
additional nine programs of interest were
identified.
• Programs were generally certificates
targeting those without a background in
computer science, though Columbia and
NYU both offer “bridge” type programs
that provide introductory coursework in
the field and prepare for a master’s
degree.
• In line with previously examined
programs, none note any focus on
increasing access to underrepresented
populations.

27
Other Competitors: Master’s programs that target those with no computer
science background may also act as competitors to iCAN.
Provider Program Name (Website Link)
MIT
Not yet
launched, new College of Computing
started
by large gift with goal of addressing “opportunities
and challenges” of computing
Northeastern University
Align MS in Computer Science
University of
Pennsylvania*
Master of Computer and Information Technology
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
*Also offered online via Coursera, program website available at this link.
Although full master’s degrees, Eduventures identified
other providers that offer master’s in computer science
programs which target those with no background in the
field, as well as a new school at MIT that may act as a
future competitor for UIUC. Notably, no programs list a
focus on increasing access to computer science for
underrepresented populations.

28
Other Competitors: MOOC platform Coursera offers few relevant
programs with little similarity to iCAN, though they have a low pricepoint
and short time to completion.
Source: https://www.coursera.org/.
‘Already Enrolled’= Starting Soon
Coursera - Relevant Courses
Provider Program Reported Outcomes Enrollment Data
Arizona State
University
Master’s – Online Master’s in
Computer Science
• Not available, though program website lists
various outcomes available to students
along with career services support
• Not listed
University of
Michigan
Specialization - Programming
for Everybody (Getting Started
with Python)
• 39% start a new career after completing
courses
• 39% get a tangible career benefit
• 12% got a pay increase or promotion
• 1,891,004 already
enrolled
University of
London
Specialization - Introduction to
Computer Programming
• 56% start a new career after completing
courses
• 42% get a tangible career benefit
• 34,018 already
enrolled
A review of Coursera offerings did not reveal
many options in line with iCAN. ASU offers a
master’s in computer science, which does not
target those without a computer science
background and is similar to UIUC’s program on
Coursera. Michigan and London offer brief,
certificate-like programs that show high
enrollment numbers.
ASU’s program is only for students
who currently hold bachelor’s in
computer science or a related field,
but students without the appropriate
background may complete a
MasterTrack Certificate that helps
students meet the prerequisites for
the program. More details available
here.

29
Other Competitors: MOOC platform edX offers more options than
Coursera targeting prospects without a relevant background.
Source: https://www.edx.org/.
Already enrolled= starting soon
Provider Program Enrollment Data
Georgia Tech Certificate - Professional Certificate in
Introduction to Python Programming
• Not listed
Harvard University Certificate - Professional Certificate in
Computer Science for Web Programming
• Not listed
Harvard University Course - CS50's Introduction to
Computer Science
• 2,455,872 already
enrolled
Harvey Mudd College Course - MyCS: Computer Science for
Beginners
• Not listed, course is
currently not available
MIT Course - Introduction to Computer
Science and Programming Using Python
• 1,263,351 already
enrolled
New York University Bachelor’s - MicroBachelors Program in
Computer Science Fundamentals
• Not listed
Stanford University Course - Computer Science 101 • 39,984 already enrolled
University of Texas at
Austin
Master’s - Master’s Degree in Computer
Science
• Not listed
edX - Relevant Courses
Eduventures also examined offerings at edX which
reveals several options representing a mix of
certificates, courses, and degree programs (bachelor’s
and master’s). NYU’s micro-bachelor’s offering is
especially interesting as it providers undergraduate-
level coursework in the field, which is in line with
iCAN’s offering. Offerings from Harvard and MIT see
particularly strong enrollments.
Though a bachelor’s level program, this
option may appeal to prospects who wish to
start from a lower level of instruction in the
field. The program targets those without a
background in the field.
Similar to ASU’s program offered via
Coursera, UT’s program requires that
students have a bachelor’s in computer
science or related, although exceptions may
be made. More details available here.

Competitive Insights
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

31
Competitive Insights: Competitors chosen for analysis.
Institution Program Name
(Website Link)
Modality Notes Rationale for Selection
Columbia University
CS@CU MS Bridge Program in
Computer Science
Unclear
•
Similarity to iCAN program
•
Target audience and program outcomes in
line with iCAN
•
Unique program approach
Drexel University
Online Certificate in Computer Science
100% online modality
•
Similarity to iCAN program
•
Target audience and program outcomes in
line with iCAN
•
Online modality
Harvard Extension
School
Programming Certificate Unclear
•
Some similarity to iCAN program
•
Target audience in line with iCAN
Seattle University
Computer Science Fundamentals
Graduate Certificate
On-campus, part-
time program that
meets twice a week
•
Solid conferral rates, top provider of post
baccalaureate certificates
•
Similarity to iCAN program
•
Target audience and program outcomes in
line with iCAN
Tufts
University
Postbaccalaureate in Computer
Science
On-campus, full-time program
•
Similarity to iCAN program
•
Target audience and program outcomes in
line with iCAN
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
• Eduventures selected five programs to gain
insights into the market. The selection was
based on similarity to the iCAN program (target
audience, program outcomes), as well as other
factors like uniqueness of program and
conferrals rates.
• Modality varied with some programs not giving
clear information and others meeting on-
campus. Drexel is the only examined program
that offers their program via 100% online
modality.
• Columbia’s program, though different from
iCAN, is titled and marketed differently than
other examined programs and is worth
considering.

32
Competitive Insights: Program characteristics show programs are
usually one year and often lead to master’s degrees.
Institution # of
Credits
Graduate Credits Earned? Program Length Admissions Notes
Columbia University
14-17*
Yes
- Students can go on to the MS
program at Columbia upon
completion
One
year- Summer/fall/spring
part
-time study
No
computer science or
programming experience
required, only bachelor’s degree
Drexel University
15^
Yes
- Students can enroll
in master’s
program upon completion
One
year-
Fall/winter/spring/summer
program (10
-week quarters)
No
computer science or
programming experience
required, only bachelor’s degree
Harvard Extension School
4 courses
Yes
-
Courses taken are for graduate
credit but cannot be applied to
technology master’s degree
1.5
years- Average number of
years it takes to complete
certificate
No
application required, only
enrollment in aligned courses
Seattle University
18-24**
Yes
-
Students can enroll in master’s
program upon completion
~One
year-
Winter/spring/summer/fall/winter
(Boot camp in first winter, may be
waived for students with
experience)
No
computer science or
programming experience
required, only bachelor’s degree
Tufts
University
14-17^^
Yes
-
Students can enroll in master’s
program upon completion though
undergraduate level coursework
does not count towards master’s
One
year- Program can be
completed in two semesters or
full
-time study or spread out
Bachelor’s and one
college-level
introductory computer course
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
*14 credits for students with a technical background, 17 for those without as they are recommended to take an additional math course
^Program notes it is a 12-credit certificate but curriculum page lists 15-credits
**Two bootcamp courses are equal to six credits, which is not required for all students but is helpful for students with no background in computer science. Program is 18 credits without
bootcamp
^^Number of credits depends on specific coursework selection
• A review of program characteristics reveals
that the number of credits ranges from 14-
24, depending on curriculum. Harvard
Extension School does not include the
number of credits but its four required
courses are in line with the other providers.
• All programs appear to grant credit for
graduate coursework and note that
students can move into their master’s
degree program upon completion.
Interestingly, Harvard Extension School
notes their coursework is for graduate
credit but that students cannot apply it
towards a technology-related master’s
degree at the school.
• Time to completion was typically about one
year but often included three or four
semesters of study. Admissions typically
required just a bachelor’s degree with only
Tufts requiring a college-level computer
science course.
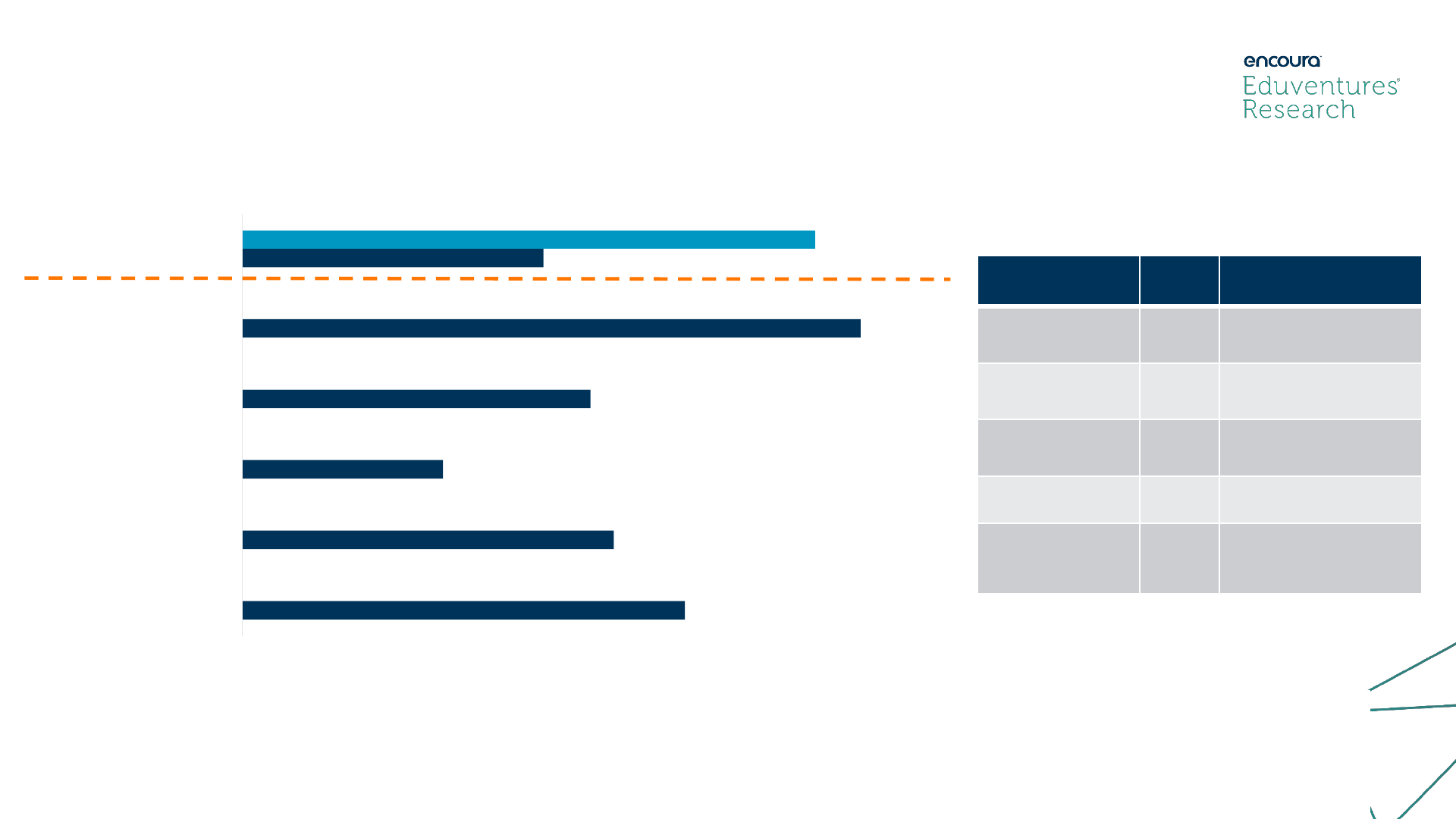
33
Estimated total tuition of examined programs range from between roughly $11,000 and $36,000 with most falling
towards the middle of the range. Harvard Extension School had the lowest total estimated cost while Columbia had
the highest cost.
Providers # of
Credits
Pricing per Credit
Columbia University
17^ $2,104
Drexel University
15 $1,342
Harvard Extension
School
Not
listed
Not listed – only
average cost provided
Seattle University
24^^ $895
Tufts University
17*** • Undergrad-level:
$690
• Grad-level: $1,697
Source: Program and Institutional Websites
*Tuition per credit includes stated tuition per credit without additional fees (e.g. Student Financial Fee) unless otherwise noted. Eduventures analyzes tuition by base per credit to ensure an aligned comparison among all competitors. Tuition is for both
in-state and out-of-state students unless otherwise noted.
**Please note that the purpose of this pricing data is to provide initial insight into the competitive pricing landscape; additional differences and variances may arise should Eduventures conduct a deeper pricing analysis on this data, though
Eduventures estimates that these variances would be slight.
^Although the program can be completed with 14 credits for those with a non-technical background, Eduventures provides the cost for the 17 credit option for those without a background in the field
^^Without bootcamp coursework, program is 18 credits but Eduventures provides the total estimated cost of the program with the bootcamp courses
***In line with other examined programs, Eduventures selected the higher number of credits for this particular program and also estimated tuition at the highest possible cost (two undergrad level and three grad level courses)
Competitive Analysis: Tuition insight* reveals iCAN in-state in line with
most programs, but out-of-state cost higher than almost all.
$25,597
$21,480
$11,600
$20,130
$35,768
$17,418
$33,142
$0 $5,000 $10,000 $15,000 $20,000 $25,000 $30,000 $35,000 $40,000
Tufts University
Seattle University
Harvard Extension School
Drexel University
Columbia University
UIUC iCAN
Estimated Total Tuition**

34
Competitive Insights: Target audience
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
Institution Target Audience Notes
Columbia University
• Those without a computer science background or
programming experience
•
Those who wish to enter the field of technology
Drexel University
•
Those who wish to refresh
a resume or gain new
skills
• Those who wish to enter a master’s program in a
related field
Harvard Extension School
•
Those with little to no computer programming or
language experience
Seattle University
• Working professionals who wish to make a career
change to the tech field
•
Anyone with a bachelor’s degree
Tufts
University
•
Those who wish to advance or change careers
•
Those preparing for graduate school
Target audience typically noted those
without a computer science
background who are looking for a
career change or advancement.
Seattle emphasized their focus on
working professionals.

35
Competitive Insights: Marketing themes
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
Institution Marketing Notes
Columbia University
•
Customizable curriculum based on students’ interest
•
Pathway to master’s degree program
•
Faculty involvement in program from computer
science department
Drexel University
•
Gain new skills in field to advance career
•
Entry point to master’s degree in related field
•
Strong career outcomes with salaries listed
•
Online modality for working professionals
Harvard Extension School
•
Range of skills gained through the program
•
Flexibility of program with no application process
•
Low cost of program
Seattle University
•
Program is for those who wish to make a career
change to the tech field
•
Flexible program for working professionals
•
Faculty involvement from those with extensive
experience in the field
•
Potential to enroll in master’s degree program
following completion of certificate
Tufts
University
•
Flexible program for students with range of potential
outcomes including enrolling in master’s program
•
Application can be for certificate or joint
certificate/master’s program
•
Enrollment in “same high quality courses” as Tufts
undergraduates and graduates
Marketing themes vary by program
with most focusing on career
outcomes or skills gained. The
pathway to a master’s degree was
another common theme.

36
Competitive Insights: Outcomes
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
Institution Outcomes Notes
Columbia University
•
Vague note on careers in technology
•
Computer science MS program at Columbia
Drexel University
•
Notes skills from program can help or advance
career
•
Lists potential fields to use skills and salary
outcomes of aligned job titles
Harvard Extension School
•
Skills gained via the program are clearly listed
•
Notes that program is helpful introduction to
master’s degrees
Seattle University
•
General notes on entering technology field for
career
• Master’s program is general outcome with 89% of
graduates taking that path
Tufts
University
•
Career advancement or career change
•
Entrance into graduate school
Though career benefits were frequently noted, clear
outcomes were not generally given besides the
potential for entering a master’s program. Drexel had
the most details on specific career outcomes with
sectors, roles, and salary information provided.

37
Competitive Insights: Curriculum notes
Source: Institutional and Programmatic Websites
Columbia University
Drexel
University
Harvard Extension School
Seattle
University
Tufts University
Required
(4):
•
Intro to CS and
Programming in Java
•
Data Structures
•
Advanced
Programming
•
Discrete Mathematics
Recommended Math
Foundational Course
(choose 1):
•
Computer Science
Theory
•
Fundamental of
Computer Systems
Required (4):
•
Introduction to
Programming
•
Data Structures and
Algorithm
•
Systems Basics
•
Introduction to
Software Design
Electives (1) Sample
:
•
Introduction to
Artificial Intelligence
•
Developing User
Interfaces
•
Programming
Languages
•
Machine Learning
•
Web Services and
Mobile Architectures
Two Tracks in Program:
Track 1: Computer Science:
Required (3)
:
•
Intensive Introduction to
Computer Science
•
Data Structures
•
Elective of choice from
group
Track 2: Computer Science
and Java:
Required (3)
:
•
Introduction to Computer
Science Using Java I OR
Great Ideas in Computer
Science in Java
•
Introduction to Computer
Science Using Java II
•
Data Structures
•
Elective of choice from
group
Bootcamp
(2 courses):
• Required for those who
have not completed
programming
coursework
•
Programming I
•
Programming II
Required (6):
•
Database Systems
•
Special Topics: Data
Structures
•
Object-Oriented
Concepts
•
Computing Systems
Principles I
•
Algorithms
•
Computing Systems
Principles II
Required (3):
•
Data Structures
•
Discrete Math
•
Elective of choice from
group
Required (choose 2)
:
•
Computer Architecture
and Assembly
Language
Programming
•
Programming
Languages
•
Algorithms
•
Theory of Computation
Most programs had a set of
somewhat similar core courses with
a couple offering flexibility in
electives or via pathways.

Labor Market Demand
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

39
Labor Market Demand: Aligned occupations shows range of positions
and bachelor’s degree as most common degree for entry.
SOC Description
Illustrative Examples Typical Education
Needed for Entry
15-1111 Computer and Information Research
Scientists
Computational Theory Scientist; Control System Computer Scientist;
Programming Methodology and Languages Researcher
Master’s Degree
11-3031 Computer and Information Systems
Managers
Chief Technology Officer; Information Technology Systems Director;
Management Information Systems Director
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1241 Computer Network Architects
Computer Network Engineer; Network Designer; Network Developer
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1152 Computer Network Support Specialists
Network Diagnostic Support Specialist; Network Support Technician;
Network Technician
Associate’s Degree
15-1131 Computer Programmers
Applications Programmer; Computer Language Coder; IT
Programmer; Systems Programmer
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1211 Computer Systems Analysts
Applications Analyst, Data Processing Systems Analyst, Information
Systems Analyst, Systems Architect
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1242 Database Administrators
Database Programmer, Database Security Administrator
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1122 Information Security Analysts
Computer Security Specialist; IT Risk Specialist; Network Security
Analyst
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1142 Network and Computer Systems
Administrators
Network Analyst, Network Coordinator, Wide Area Network
Administrator
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1132 Software Developers
Computer Applications Engineer; Computer Systems Engineer;
Mobile Applications Developer; Software Applications Architect;
Software Engineer; Systems Software Developer
Bachelor’s Degree
15-1134 Web Developers
Intranet Developer; Web Applications Developer; Web Architect
Associate’s Degree
Source: BLS through Emsi
Eduventures examined
illustrative job titles and typical
education needed for entry
into relevant occupations.
These occupations give
insights into specific positions
potentially available to
graduates of the program.
Additionally, bachelor’s
degrees are the usual degree
of entry into these
occupations. This will be
helpful for the iCAN program,
which will equip bachelor’s
degree holders with relevant
skills for many of these
positions.

40
Labor Market Demand: Nationally, aligned occupations show projected
growth in line or above the average.
Occupational Data: National
SOC Description
2020 Jobs 2030 Jobs 2020-2030
Change
2020-2030 %
Change
All SOC Codes All Occupations
155,302,211
167,265,136
11,962,925
8%
15-1111 Computer and Information Research Scientists
34,190 40,329 6,139 18%
11-3031 Computer and Information Systems Managers
448,267 506,047 57,780 13%
15-1241 Computer Network Architects
154,805 166,940 12,135 8%
15-1152 Computer Network Support Specialists
201,519 219,081 17,562 9%
15-1131 Computer Programmers
197,137 191,522 -5,615 -3%
15-1211 Computer Systems Analysts
600,704 664,100 63,396 11%
15-1242 Database Administrators
126,900 142,071 15,171 12%
15-1122 Information Security Analysts
134,534 172,657 38,123 28%
15-1142 Network and Computer Systems Administrators
360,404 388,479 28,075 8%
15-1132 Software Developers
1,462,399 1,767,284 304,885 21%
15-1134 Web Developers
152,821 176,027 23,206 15%
Source: BLS through Emsi
Computer Programmers is the
only occupation that shows
projected declines in growth of
all the examined occupations.
Information Security Analysts
and Software Developers had
the fastest projected growth of
the aligned occupations,
although Information Security
Analysts may be less relevant
for the iCAN program.

41
Labor Market Demand: In line with the national market, aligned
occupations are generally similar to or exceed the regional average.
Occupational Data: Regional
Source: BLS through Emsi
Region defined as the following states: IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, OH, WI
SOC Description
2020 Jobs 2030 Jobs 2020-2030
Change
2020-2030 %
Change
All SOC Codes All Occupations
32,255,707
33,445,463
1,189,756
4%
15-1111 Computer and Information Research Scientists
3,093
3,619
526
17%
11-3031 Computer and Information Systems Managers
80,054 86,822 6,768 8%
15-1241 Computer Network Architects
27,004 27,901 879 3%
15-1152 Computer Network Support Specialists
43,183 44,847 1,665 4%
15-1131 Computer Programmers
36,367 33,572 -2,795 -8%
15-1211 Computer Systems Analysts
138,073 144,356 6,283 5%
15-1242 Database Administrators
22,301 24,032 1,731 8%
15-1122 Information Security Analysts
21,002 26,156 5,154 25%
15-1142 Network and Computer Systems Administrators
64,687 67,196 2,509 4%
15-1132 Software Developers
259,424 299,008 39,584 15%
15-1134 Web Developers
27,429 29,892 2,463 9%
The regional market again
shows that Information Security
Analysts had the strongest
growth of aligned occupations,
though Software Developers
has slower projected growth.
Computer Programmers also
had a projected decline in jobs
and is the only aligned
occupation to show negative
growth.

Prospective Adult Students
Illinois Computer Accelerator for Non-Specialists (iCAN) Non-Degree Program

43
Adult Prospective Students- Findings from Eduventures June 2020
Adult Prospect Survey.
Eduventures launched a survey in June 2020 to over 2,000 prospective adult students in order to capture insights into
their preferences following the outbreak of COVID-19 in March 2020. Over the following four slides, insights into relevant
questions are provided.
In order to gain more insights into potential prospects for the iCAN program, Eduventures included responses from adult
prospects interested in undergraduate or graduate certificates (n=124 respondents) and compared their responses to the
entire sample of all prospective adults (n=2,270).
To gauge modality preferences (slide 44), Eduventures asked a series of three questions to measure change in modality
preferences from adult prospects prior to COVID-19, over the next few months, and in six months or more (when the
outbreak may have passed). For the other questions (on slides 45-47), Eduventures included insights on responses from
the 2019 survey where relevant.

44
Adult Prospective Students: Strong increase in online modality
preference during COVID and potentially beyond COVID.
Source: 2020 June Adult Prospect Survey
Interested in Undergraduate or Graduate Certificates: 124 Participants
If you were to enroll in a college or university, how would you prefer to participate?
13%
6%
10%
31%
13%
20%
17%
18%
21%
22%
28%
23%
18%
36%
27%
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
Before COVID-19 Next Few Months Six Months or More
On-campus Mostly on-campus An even mix Mostly online Online
Compared to before COVID-19, online
modality for prospects interested in
certificate programs increases significantly
and remains higher in six months or more.
On-campus or mostly on-
campus modality interest is
lower than before COVID-19
with increased interest in an
even mix or mostly online
modality.

45
Prospective Adult Students: Earning more money is the top career expectation
for certificate prospects, though getting a better job or switching careers are other
top expectations.
Q) What are the top three career expectations you have for continuing your education?
16%
15%
20%
27%
24%
26%
57%
12%
16%
22%
23%
30%
31%
61%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70%
Obtain scientific, mathematical, or technical skills
Get a better job with my current employer
Improve my current job performance
Build a solid foundation for my entire career
Switch careers
Get a better job in the same industry or profession
Earn more money
Interested in certificates All prospective adult students
Source: 2020 June Adult Prospect Survey
National Sample: 2,270 Participants
Interested in Undergraduate or Graduate Certificates: 124 Participants
Getting a better job in the same
industry/profession and switching careers
are two other important career
expectations for certificate prospects.
These prospects select the two options at
a higher rate than the rest of the sample.
All prospects and prospects interested in
certificate programs both select that
earning more money is their top career
expectation, although this is selected at a
slightly higher rate by certificate prospects.

46
Prospective Adult Students: While affordable tuition and fees is the top
feature, customizable content is also important.
Source: 2020 June Adult Prospect Survey
National Sample: 2,270 Participants
Interested in Undergraduate or Graduate Certificates: 124 Participants
Q) What are the top three features you care about the most when selecting a degree or certificate program?
17%
20%
25%
24%
31%
34%
53%
19%
22%
24%
25%
26%
37%
53%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60%
Access to career services
Receive credit for life and work experience
Evidence of program quality
Financial aid and / or student debt forgiveness options
Options to work at my own pace
Programs and courses customized to my needs & goals
Affordable tuition and fees
Interested in certificates All prospective adult students
Affordable tuition and fees are the top
feature for both the entire sample, as
well as for adult prospects interested in
certificate programs. Customized
programs and courses are the other
top feature for both populations,
although prospects interested in
certificate programs select this option
at a slightly higher rate.

47
Prospective Adult Students: Faculty interactions is the most important
experience, followed by academically rigorous coursework.
Source: 2020 June Adult Prospect Survey
National Sample: 2,270 Participants
Interested in Undergraduate or Graduate Certificates: 124 Participants
Q) What are the top three experiences you expect to learn the most from while continuing your education?
26%
20%
34%
26%
32%
33%
45%
22%
24%
25%
31%
31%
35%
46%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
Participating in social and cultural events
Collaborating with students on projects
Interacting with students in my field of interest
Interacting with students with different life experiences
Obtaining an internship / practicum or other work
experience
Rigorous academic coursework
Interacting with faculty in my field of interest
Interested in certificates All prospective adult students
Interacting with faculty is the top experience
for prospects interested in certificate
programs, which is in line with the national
sample. Rigorous academic coursework and
obtaining an internship/practicum are other
top experiences.
Students interested in certificate programs
value interactions with other students,
including those with different life
experiences and those in their field of
interest. They also value collaborating with
students on projects.

ENCOURA.ORG
Thank you.
